_targeting CD19 in B-cell lymphoma: emerging role of SAR3419
- PMID: 24023523
- PMCID: PMC3767487
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S45957
_targeting CD19 in B-cell lymphoma: emerging role of SAR3419
Abstract
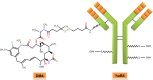
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma symbolizes a heterogeneous group of diseases resulting from malignant transformation of lymphocytes with differing patterns of behavior and responses to treatment. The potential curability of non-Hodgkin lymphoma differs among the various histologic subtypes and is associated in part with the stage at presentation. CD19 antigen is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin Ig superfamily. CD19 is specifically expressed in normal and neoplastic B-cells. Recent study showed that in a mouse model, CD19 and c-Myc synergize functionally to accelerate B-cell lymphomagenesis, which is associated with increased disease severity. Specificity is the most important challenge in cancer therapeutics. Antibody-drug conjugates have the prospect of enhancing the therapeutic efficacy over unconjugated monoclonal antibodies through the selective delivery of cytotoxic agents to cancer cells. The ubiquitous expression of CD19 in these tumors, especially at an earlier stage and the property of efficient internalization, makes CD19 an attractive and affective _target for antibody-drug conjugate therapy as compared to CD20. SAR3419 (huB4-DM4) is a novel antibody-drug conjugate that is composed of a humanized monoclonal IgG1 anti-CD19 antibody (huB4) attached to the potent cytotoxic drug, a maytansine derivative (DM4), through a cleavable disulfide cross-linking agent N-Succinimidyl-4-2-pyridyldithio butanoic acid (SPDB). The preclinical efficacy of maytansine derivative-anti-CD19 conjugate was demonstrated in our laboratory, and SAR3419 was found to be more effective than CHOP in a xenograft model. Phase I trials have also been conducted on the basis of preclinical studies that demonstrated promising antitumor activity with acceptable safety results in human B-cell lymphoma models. Additional trials are ongoing and will provide additional insight into the full potential of this novel drug.
Keywords: SAR3419; antibody-drug conjugates (ADC); lymphoma; maytansinoids; microtubule inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design of Coltuximab Ravtansine, a CD19-_targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies: Structure-Activity Relationships and Preclinical Evaluation.Mol Pharm. 2015 Jun 1;12(6):1703-16. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00175. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Mol Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25856201
-
The novel CD19-_targeting antibody-drug conjugate huB4-DGN462 shows improved anti-tumor activity compared to SAR3419 in CD19-positive lymphoma and leukemia models.Haematologica. 2019 Aug;104(8):1633-1639. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.211011. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30733273 Free PMC article.
-
SAR3419: an anti-CD19-Maytansinoid Immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 15;17(20):6448-58. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0485. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22003072 Review.
-
Superior antitumor activity of SAR3419 to rituximab in xenograft models for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Jun 15;15(12):4038-45. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2808. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19509168
-
Development and Integration of Antibody-Drug Conjugate in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2015 Sep;17(9):41. doi: 10.1007/s11912-015-0466-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26194424 Review.
Cited by
-
Gemcitabine-(5'-phosphoramidate)-[anti-IGF-1R]: molecular design, synthetic organic chemistry reactions, and antineoplastic cytotoxic potency in populations of pulmonary adenocarcinoma (A549).Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017 Mar;89(3):379-399. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12845. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017. PMID: 27561602 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of novel _target genes and pathways involved in bevacizumab-resistant colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 17;13(1):e0189582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189582. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29342159 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CD19 Monoclonal Antibodies: a New Approach to Lymphoma Therapy.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2015 Summer;4(3):143-51. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2015. PMID: 26629482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status and perspectives of chimeric antigen receptor modified T cells for cancer treatment.Protein Cell. 2017 Dec;8(12):896-925. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0400-z. Epub 2017 May 2. Protein Cell. 2017. PMID: 28466386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of AFM11 in the treatment of patients with B-cell malignancies: findings from two phase 1 studies.Trials. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06982-7. Trials. 2023. PMID: 36597128 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. - PubMed
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al.SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations) [webpage on the Internet]Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2011[updated Apr 2012]. Available from: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/Assessed July 10, 2013
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC; 2008.
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood. 2008;111(12):5446–5456. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, et al. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom’sMacroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol. 2003;30(2):110–115. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

