Evaluation of the success criteria for zirconia dental implants: a four-year clinical and radiological study
- PMID: 24065992
- PMCID: PMC3770060
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/463073
Evaluation of the success criteria for zirconia dental implants: a four-year clinical and radiological study
Abstract
Objectives. The aim was to evaluate survival and success rates, soft tissue health, and radiographic marginal bone loss (MBL) of zirconia implants placed in the esthetic and posterior areas of the jaws and in association with multiple or single implant restorations after at least 6 months of definitive restoration. Material and Methods. 35 one-piece zirconium implants were utilized for single or partially edentulous ridges rehabilitation. All implants received immediate temporary restorations and six months after surgery were definitively restored. Every 6 months after implant placement, a clinical-radiographic evaluation was performed. For each radiograph, the measurements of MBL were calculated. Results. The results showed that the mean MBL at 48-month followup was 1.631 mm. The mean MBL during the first year of loading was not more significant for implants placed in the first molar regions than for those positioned in other areas. Moreover, no differences in marginal bone level changes were revealed for multiple and single implants, whereas MBL in the first year was observed to be slightly greater for implants placed in the maxilla than for those placed in the mandible. Conclusion. Zirconia showed a good marginal bone preservation that could be correlated with one-piece morphology and characteristics of zirconia implants.
Figures

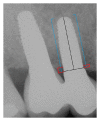
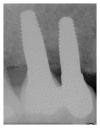
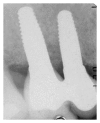
Similar articles
-
Zirconia implants: a promising alternative to titanium?Evid Based Dent. 2021 Jan;22(3):102-103. doi: 10.1038/s41432-021-0202-2. Evid Based Dent. 2021. PMID: 34561660
-
One-piece zirconia oral implants: one-year results from a prospective case series. 2. Three-unit fixed dental prosthesis (FDP) reconstruction.J Clin Periodontol. 2013 May;40(5):553-62. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12093. Epub 2013 Mar 18. J Clin Periodontol. 2013. PMID: 23506654
-
Multiple teeth replacement with endosseous one-piece yttrium-stabilized zirconia dental implants.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012 Nov 1;17(6):e981-7. doi: 10.4317/medoral.18194. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012. PMID: 22926479 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the clinical outcome of zirconia implant-restoration complex.J Prosthodont Res. 2018 Oct;62(4):397-406. doi: 10.1016/j.jpor.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Jul 5. J Prosthodont Res. 2018. PMID: 29983377 Review.
-
The fate of marginal bone around axial vs. tilted implants: a systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2014 Summer;7 Suppl 2:S171-89. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2014. PMID: 24977252 Review.
Cited by
-
Success and patient satisfaction of immediately loaded zirconia implants with fixed restorations one year after loading.BMC Oral Health. 2022 May 23;22(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02231-0. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35606734 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Stability of Hydrothermally Aged and/or Dynamically Loaded One-Piece Diameter Reduced Zirconia Oral Implants.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Feb 24;14(3):123. doi: 10.3390/jfb14030123. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36976047 Free PMC article.
-
Single tooth restoration in the maxillary esthetic zone using a one-piece ceramic implant with 1 year of follow-up: case series.Int J Implant Dent. 2021 Apr 6;7(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40729-021-00308-z. Int J Implant Dent. 2021. PMID: 33821399 Free PMC article.
-
Zirconium dioxide implants as an alternative to titanium: A systematic review.J Clin Exp Dent. 2021 May 1;13(5):e511-e519. doi: 10.4317/jced.58063. eCollection 2021 May. J Clin Exp Dent. 2021. PMID: 33981400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A prospective clinical study to evaluate the performance of zirconium dioxide dental implants in single-tooth edentulous area: 3-year follow-up.BMC Oral Health. 2018 Nov 1;18(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12903-018-0636-x. BMC Oral Health. 2018. PMID: 30382850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brånemark PI, Adell R, Breine U, Hansson BO, Lindström J, Ohlsson A. Intra-osseous anchorage of dental prostheses. I. Experimental studies. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1969;3(2):81–100. - PubMed
-
- Leben M Goiato JD, Gennari-Filho H, Assun OW, Dos Santos D. Esthetics in implant-supported prostheses—a literature review. Journal of Oral Implantology. 2012;38(6):718–722. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa-Nagai S, Da Silva JD, Weber HP, Park SE. Optical phenomenon of peri-implant soft tissue. Part II. preferred implant neck color to improve soft tissue esthetics. Clinical Oral Implants Research. 2007;18(5):575–580. - PubMed
-
- Bengazi F, Wennström JL, Lekholm U. Recession of the soft tissue margin at oral implants: a 2-year longitudinal prospective study. Clinical Oral Implants Research. 1996;7(2):303–310. - PubMed
-
- Lalor PA, Revell PA, Gray AB, Wright S, Railton GT, Freeman MAR. Sensitivity to titanium. A cause of implant failure? Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery B. 1991;73(1):25–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

