Molecular mechanism of GTPase activation at the signal recognition particle (SRP) RNA distal end
- PMID: 24151069
- PMCID: PMC3868752
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.513614
Molecular mechanism of GTPase activation at the signal recognition particle (SRP) RNA distal end
Abstract
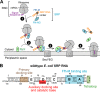
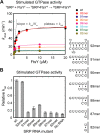
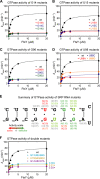
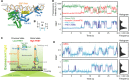
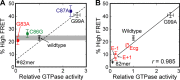
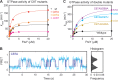
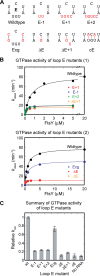
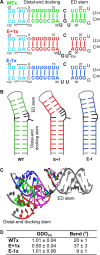
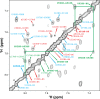
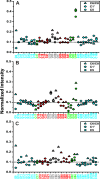
The signal recognition particle (SRP) RNA is a universally conserved and essential component of the SRP that mediates the co-translational _targeting of proteins to the correct cellular membrane. During the _targeting reaction, two functional ends in the SRP RNA mediate distinct functions. Whereas the RNA tetraloop facilitates initial assembly of two GTPases between the SRP and SRP receptor, this GTPase complex subsequently relocalizes ∼100 Å to the 5',3'-distal end of the RNA, a conformation crucial for GTPase activation and cargo handover. Here we combined biochemical, single molecule, and NMR studies to investigate the molecular mechanism of this large scale conformational change. We show that two independent sites contribute to the interaction of the GTPase complex with the SRP RNA distal end. Loop E plays a crucial role in the precise positioning of the GTPase complex on these two sites by inducing a defined bend in the RNA helix and thus generating a preorganized recognition surface. GTPase docking can be uncoupled from its subsequent activation, which is mediated by conserved bases in the next internal loop. These results, combined with recent structural work, elucidate how the SRP RNA induces GTPase relocalization and activation at the end of the protein _targeting reaction.
Keywords: G Proteins; Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; Protein _targeting; Protein-Nucleic Acid Interaction; RNA; Single Molecule Biophysics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The crystal structure of the signal recognition particle in complex with its receptor.Science. 2011 Feb 18;331(6019):881-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1196473. Science. 2011. PMID: 21330537 Free PMC article.
-
SRP RNA provides the physiologically essential GTPase activation function in cotranslational protein _targeting.RNA. 2007 Feb;13(2):240-50. doi: 10.1261/rna.135407. Epub 2006 Dec 12. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17164479 Free PMC article.
-
Fingerloop activates cargo delivery and unloading during cotranslational protein _targeting.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jan;24(2):63-73. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-06-0434. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23135999 Free PMC article.
-
Co-translational protein _targeting by the signal recognition particle.FEBS Lett. 2005 Feb 7;579(4):921-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.049. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15680975 Review.
-
Structural insights into the signal recognition particle.Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:539-57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074048. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15189152 Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstitution of the human SRP system and quantitative and systematic analysis of its ribosome interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 8;47(6):3184-3196. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1324. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30649417 Free PMC article.
-
Signal recognition particle-ribosome binding is sensitive to nascent chain length.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 11;289(28):19294-305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.563239. Epub 2014 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24808175 Free PMC article.
-
Co-evolution of Two GTPases Enables Efficient Protein _targeting in an RNA-less Chloroplast Signal Recognition Particle Pathway.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 6;292(1):386-396. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.752931. Epub 2016 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27895118 Free PMC article.
-
The completed genome sequence of the pathogenic ascomycete fungus Fusarium graminearum.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 22;16(1):544. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1756-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26198851 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Single-Molecule Protein Transportation Experiments via Hierarchical Hidden Markov Models.J Am Stat Assoc. 2016;111(515):951-966. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2016.1140050. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Am Stat Assoc. 2016. PMID: 28943680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keenan R. J., Freymann D. M., Stroud R. M., Walter P. (2001) The signal recognition particle. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 755–775 - PubMed
-
- Walter P., Johnson A. E. (1994) Signal sequence recognition and protein _targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 87–119 - PubMed
-
- Halic M., Becker T., Pool M. R., Spahn C. M., Grassucci R. A., Frank J., Beckmann R. (2004) Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome. Nature 427, 808–814 - PubMed
-
- Halic M., Blau M., Becker T., Mielke T., Pool M. R., Wild K., Sinning I., Beckmann R. (2006) Following the signal sequence from ribosomal tunnel exit to signal recognition particle. Nature 444, 507–511 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

