Effects of interval and continuous exercise training on CD4 lymphocyte apoptotic and autophagic responses to hypoxic stress in sedentary men
- PMID: 24236174
- PMCID: PMC3827435
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080248
Effects of interval and continuous exercise training on CD4 lymphocyte apoptotic and autophagic responses to hypoxic stress in sedentary men
Abstract
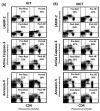
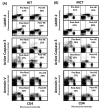
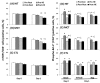
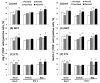
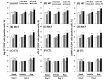
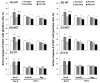
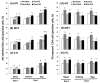
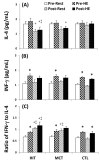
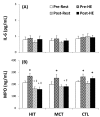
Exercise is linked with the type/intensity-dependent adaptive immune responses, whereas hypoxic stress facilitates the programmed death of CD4 lymphocytes. This study investigated how high intensity-interval (HIT) and moderate intensity-continuous (MCT) exercise training influence hypoxia-induced apoptosis and autophagy of CD4 lymphocytes in sedentary men. Thirty healthy sedentary males were randomized to engage either HIT (3-minute intervals at 40% and 80%VO2max, n=10) or MCT (sustained 60%VO2max, n=10) for 30 minutes/day, 5 days/week for 5 weeks, or to a control group that did not received exercise intervention (CTL, n=10). CD4 lymphocyte apoptotic and autophagic responses to hypoxic exercise (HE, 100 W under 12%O2 for 30 minutes) were determined before and after various regimens. The results demonstrated that HIT exhibited higher enhancements of pulmonary ventilation, cardiac output, and VO2 at ventilatory threshold and peak performance than MCT did. Before the intervention, HE significantly down-regulated autophagy by decreased beclin-1, Atg-1, LC3-II, Atg-12, and LAMP-2 expressions and acridine orange staining, and simultaneously enhanced apoptosis by increased phospho-Bcl-2 and active caspase-9/-3 levels and phosphotidylserine exposure in CD4 lymphocytes. However, five weeks of HIT and MCT, but not CTL, reduced the extents of declined autophagy and potentiated apoptosis in CD4 lymphocytes caused by HE. Furthermore, both HIT and MCT regimens manifestly lowered plasma myeloperoxidase and interleukin-4 levels and elevated the ratio of interleukin-4 to interferon-γ at rest and following HE. Therefore, we conclude that HIT is superior to MCT for enhancing aerobic fitness. Moreover, either HIT or MCT effectively depresses apoptosis and promotes autophagy in CD4 lymphocytes and is accompanied by increased interleukin-4/interferon-γ ratio and decreased peroxide production during HE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interval and continuous exercise regimens suppress neutrophil-derived microparticle formation and neutrophil-promoted thrombin generation under hypoxic stress.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Apr;128(7):425-36. doi: 10.1042/CS20140498. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25371035 Clinical Trial.
-
High-intensity Interval Training Improves Mitochondrial Function and Suppresses Thrombin Generation in Platelets undergoing Hypoxic Stress.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 23;7(1):4191. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04035-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28646182 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High-intensity Interval training enhances mobilization/functionality of endothelial progenitor cells and depressed shedding of vascular endothelial cells undergoing hypoxia.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016 Dec;116(11-12):2375-2388. doi: 10.1007/s00421-016-3490-z. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27761657 Clinical Trial.
-
The Use of Simulated Altitude Techniques for Beneficial Cardiovascular Health Outcomes in Nonathletic, Sedentary, and Clinical Populations: A Literature Review.High Alt Med Biol. 2017 Dec;18(4):305-321. doi: 10.1089/ham.2017.0050. Epub 2017 Aug 28. High Alt Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28846046 Review.
-
Meta-analysis of aerobic interval training on exercise capacity and systolic function in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fractions.Am J Cardiol. 2013 May 15;111(10):1466-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.01.303. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Am J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23433767 Review.
Cited by
-
Moderate Aerobic Training Improves Cardiorespiratory Parameters in Elastase-Induced Emphysema.Front Physiol. 2016 Aug 3;7:329. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00329. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27536247 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Regular Physical Activity on the Immune System, Vaccination and Risk of Community-Acquired Infectious Disease in the General Population: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2021 Aug;51(8):1673-1686. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 33877614 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte and dendritic cell response to a period of intensified training in young healthy humans and rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 11;13:998925. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.998925. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36439269 Free PMC article.
-
The high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and curcumin supplementation can positively regulate the autophagy pathway in myocardial cells of STZ-induced diabetic rats.BMC Res Notes. 2023 Feb 25;16(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06295-1. BMC Res Notes. 2023. PMID: 36841820 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention and Rehabilitation After Heart Transplantation: A Clinical Consensus Statement of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology, Heart Failure Association of the ESC, and the European Cardio Thoracic Transplant Association, a Section of ESOT.Transpl Int. 2024 Jun 19;37:13191. doi: 10.3389/ti.2024.13191. eCollection 2024. Transpl Int. 2024. PMID: 39015154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woods JA, Davis JM, Smith JA, Nieman DC (1999) Exercises and cellular innate immune function. Med Sci Sports Exer 31: 57-66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

