Prospects for nucleic acid-based therapeutics against hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 24379620
- PMCID: PMC3870548
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8949
Prospects for nucleic acid-based therapeutics against hepatitis C virus
Abstract
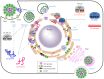
In this review, we discuss recent advances in nucleic acid-based therapeutic technologies that _target hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Because the HCV genome is present exclusively in RNA form during replication, various nucleic acid-based therapeutic approaches _targeting the HCV genome, such as ribozymes, aptamers, siRNAs, and antisense oligonucleotides, have been suggested as potential tools against HCV. Nucleic acids are potentially immunogenic and typically require a delivery tool to be utilized as therapeutics. These limitations have hampered the clinical development of nucleic acid-based therapeutics. However, despite these limitations, nucleic acid-based therapeutics has clinical value due to their great specificity, easy and large-scale synthesis with chemical methods, and pharmaceutical flexibility. Moreover, nucleic acid therapeutics are expected to broaden the range of _targetable molecules essential for the HCV replication cycle, and therefore they may prove to be more effective than existing therapeutics, such as interferon-α and ribavirin combination therapy. This review focuses on the current status and future prospects of ribozymes, aptamers, siRNAs, and antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic reagents against HCV.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotide; Aptamer; Hepatitis C virus; Nucleic acid-based therapeutics; Ribozyme; siRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
_targets and tools: recent advances in the development of anti-HCV nucleic acids.Infect Disord Drug _targets. 2006 Jun;6(2):121-45. doi: 10.2174/187152606784112182. Infect Disord Drug _targets. 2006. PMID: 16789875 Review.
-
Nucleic acids-based therapeutics in the battle against pathogenic viruses.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;189(189):243-63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79086-0_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19048203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligomeric nucleic acids as antivirals.Molecules. 2011 Jan 28;16(2):1271-96. doi: 10.3390/molecules16021271. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21278679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-based therapeutics: current progress and future prospects.Chem Biol. 2012 Jan 27;19(1):60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.12.008. Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22284355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligonucleotide-based therapeutic options against hepatitis C virus infection.Antivir Ther. 2006;11(3):273-87. Antivir Ther. 2006. PMID: 16759043 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamers in Virology-A Consolidated Review of the Most Recent Advancements in Diagnosis and Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 9;13(10):1646. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101646. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34683938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamers for Anti-Viral Therapeutics and Diagnostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 17;22(8):4168. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084168. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Composite vector formulation for multiple siRNA delivery as a host _targeting antiviral in a cell culture model of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.J Mater Chem B. 2017 Jan 28;5(4):858-865. doi: 10.1039/c6tb01718e. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Mater Chem B. 2017. PMID: 32263854 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Aptamers as Diagnostics Tools and Antiviral Agents for Human Viruses.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016 Dec 16;9(4):78. doi: 10.3390/ph9040078. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27999271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Aptamers as Molecular Tools to Study the Functionality of the Hepatitis C Virus CRE Region.Molecules. 2015 Sep 2;20(9):16030-47. doi: 10.3390/molecules200916030. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26364632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lauer GM, Walker BD. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA, Hutin YJ, Bell BP. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. J Hepatol. 2006;45:529–538. - PubMed
-
- Gottwein JM, Scheel TK, Jensen TB, Lademann JB, Prentoe JC, Knudsen ML, Hoegh AM, Bukh J. Development and characterization of hepatitis C virus genotype 1-7 cell culture systems: role of CD81 and scavenger receptor class B type I and effect of antiviral drugs. Hepatology. 2009;49:364–377. - PubMed
-
- Houghton M. Prospects for prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines against the hepatitis C viruses. Immunol Rev. 2011;239:99–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

