An EGFR/HER2-Bispecific and enediyne-energized fusion protein shows high efficacy against esophageal cancer
- PMID: 24664246
- PMCID: PMC3963964
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092986
An EGFR/HER2-Bispecific and enediyne-energized fusion protein shows high efficacy against esophageal cancer
Abstract
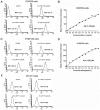
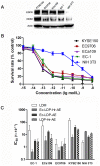
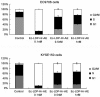
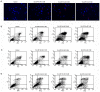
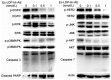
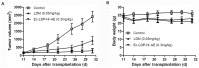
Esophageal cancer is one of the most common cancers, and the 5-year survival rate is less than 10% due to lack of effective therapeutic agents. This study was to evaluate antitumor activity of Ec-LDP-Hr-AE, a recently developed bispecific enediyne-energized fusion protein _targeting both epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), on esophageal cancer. The fusion protein Ec-LDP-Hr-AE consists of two oligopeptide ligands and an enediyne antibiotic lidamycin (LDM) for receptor binding and cell killing, respectively. The current study demonstrated that Ec-LDP-Hr had high affinity to bind to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells, and enediyne-energized fusion protein Ec-LDP-Hr-AE showed potent cytotoxicity to ESCC cells with differential expression of EGFR and HER2. Ec-LDP-Hr-AE could cause significant G2-M arrest in EC9706 and KYSE150 cells, and it also induced apoptosis in ESCC cells in a dosage-dependent manner. Western blot assays showed that Ec-LDP-Hr-AE promoted caspase-3 and caspase-7 activities as well as PARP cleavage. Moreover, Ec-LDP-Hr-AE inhibited cell proliferation via decreasing phosphorylation of EGFR and HER2, and further exerted inhibition of the activation of their downstream signaling molecules. In vivo, at a tolerated dose, Ec-LDP-Hr-AE inhibited tumor growth by 88% when it was administered to nude mice bearing human ESCC cell KYSE150 xenografts. These results indicated that Ec-LDP-Hr-AE exhibited potent anti-caner efficacy on ESCC, suggesting it could be a promising candidate for _targeted therapy of esophageal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A bispecific enediyne-energized fusion protein containing ligand-based and antibody-based oligopeptides against epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 shows potent antitumor activity.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 1;16(7):2085-94. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2699. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20332319
-
A ligand-based and enediyne-energized bispecific fusion protein _targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor shows potent antitumor efficacy against esophageal cancer.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jun;37(6):3329-3340. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5606. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28498434
-
A bispecific enediyne-energized fusion protein _targeting both epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor showing enhanced antitumor efficacy against non-small cell lung cancer.Onco_target. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):27286-27299. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.15933. Onco_target. 2017. PMID: 28460483 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in _targeted therapy for esophageal cancer.Signal Transduct _target Ther. 2020 Oct 7;5(1):229. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00323-3. Signal Transduct _target Ther. 2020. PMID: 33028804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Nuclear Receptors in Esophageal Cancer.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(12):1489-1503. doi: 10.2174/1389201024666230202155426. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36740804 Review.
Cited by
-
An EGFR/HER2-_targeted conjugate sensitizes gemcitabine-sensitive and resistant pancreatic cancer through different SMAD4-mediated mechanisms.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 20;13(1):5506. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33037-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36127339 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-_targeted Immunotoxin Exerts Antitumor Effects on Esophageal Cancers by Increasing ROS Accumulation and Inducing Apoptosis via Inhibition of the Nrf2-Keap1 Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2018 Nov 25;2018:1090287. doi: 10.1155/2018/1090287. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30596104 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-_targeting, β-defensin-tailored fusion protein exhibits high therapeutic efficacy against EGFR-expressed human carcinoma via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Nov;39(11):1777-1786. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0069-8. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 30013033 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant scFv antibody-based fusion protein that _targets EGFR associated with IMPDH2 downregulation and its drug conjugate show therapeutic efficacy against esophageal cancer.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):1243-1256. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2063454. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35416106 Free PMC article.
-
A novel antitumor dithiocarbamate compound inhibits the EGFR/AKT signaling pathway and induces apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jul;20(1):877-883. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11638. Epub 2020 May 18. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32566015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah MA, Kelsen DP (2004) Combined modality therapy of esophageal cancer: changes in the standard of care? Ann Surg Oncol 11: 641–643. Pubmed: 15197008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

