Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development
- PMID: 25419705
- PMCID: PMC4444078
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3762
Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development
Abstract
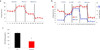
Renal fibrosis is the histological manifestation of a progressive, usually irreversible process causing chronic and end-stage kidney disease. We performed genome-wide transcriptome studies of a large cohort (n = 95) of normal and fibrotic human kidney tubule samples followed by systems and network analyses and identified inflammation and metabolism as the top dysregulated pathways in the diseased kidneys. In particular, we found that humans and mouse models with tubulointerstitial fibrosis had lower expression of key enzymes and regulators of fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and higher intracellular lipid deposition compared to controls. In vitro experiments indicated that inhibition of FAO in tubule epithelial cells caused ATP depletion, cell death, dedifferentiation and intracellular lipid deposition, phenotypes observed in fibrosis. In contrast, restoring fatty acid metabolism by genetic or pharmacological methods protected mice from tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Our results raise the possibility that correcting the metabolic defect in FAO may be useful for preventing and treating chronic kidney disease.
Figures

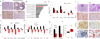





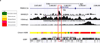
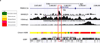
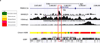
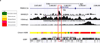
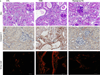



Comment in
-
Fibrosis: dysfunctional fatty acid oxidation in renal fibrosis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015 Feb;11(2):64. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.244. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25536395 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Role of the CTRP6/AMPK pathway in kidney fibrosis through the promotion of fatty acid oxidation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 5;892:173755. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173755. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33245899
-
The key role of altered tubule cell lipid metabolism in kidney disease development.Kidney Int. 2024 Jul;106(1):24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.02.025. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Kidney Int. 2024. PMID: 38614389 Review.
-
Twist1 downregulation of PGC-1α decreases fatty acid oxidation in tubular epithelial cells, leading to kidney fibrosis.Theranostics. 2022 May 1;12(8):3758-3775. doi: 10.7150/thno.71722. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35664054 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronate dysregulates fatty acid metabolism in renal tubular epithelial cells to induce nephrotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2018 Jan;92(1):469-485. doi: 10.1007/s00204-017-2048-0. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Arch Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 28871336 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling in kidney fibrosis: a master communicator.Sci China Life Sci. 2016 Sep;59(9):920-9. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-0020-y. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Sci China Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27333788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulated cell death in chronic kidney disease: current evidence and future clinical perspectives.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 31;12:1497460. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1497460. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39544363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dyna-vivo-seq unveils cellular RNA dynamics during acute kidney injury via in vivo metabolic RNA labeling-based scRNA-seq.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 14;15(1):9866. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54202-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39543112 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the cytoskeleton in fibrotic diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 24;12:1490315. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1490315. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39512901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPARs: modulating lipotoxicity and thus inhibiting fibrosis.Hormones (Athens). 2024 Nov 6. doi: 10.1007/s42000-024-00612-4. Online ahead of print. Hormones (Athens). 2024. PMID: 39500811 Review.
-
Nuclear translocation of SIRT4 mediates deacetylation of U2AF2 to modulate renal fibrosis through alternative splicing-mediated upregulation of CCN2.Elife. 2024 Nov 4;13:RP98524. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98524. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39495216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nath KA, Salahudeen AK, Clark EC, Hostetter MK, Hostetter TH. Role of cellular metabolites in progressive renal injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 1992;38:S109–S113. - PubMed
-
- Zeisberg M, et al. BMP-7 counteracts TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat Med. 2003;9:964–968. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

