Comprehensive craniospinal radiation for controlling central nervous system leukemia
- PMID: 25539370
- PMCID: PMC4868499
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.08.004
Comprehensive craniospinal radiation for controlling central nervous system leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the benefit of radiation therapy (RT) in resolution of neurologic symptoms and deficits and whether the type of RT fields influences central nervous system (CNS) control in adults with CNS leukemia.
Methods and materials: A total of 163 adults from 1996 to 2012 were retrospectively analyzed. Potential associations between use of radiation and outcome were investigated by univariate and multivariate analysis.
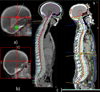
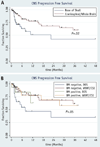
Results: The median survival time was 3.8 months after RT. Common presenting symptoms were headache in 79 patients (49%), cranial nerve VII deficit in 46 (28%), and cranial nerve II deficit in 44 (27%). RT was delivered to the base of skull in 48 patients (29%), to the whole brain (WB) in 67 (41%), and to the craniospinal axis (CS) in 48 (29%). Among 149 patients with a total of 233 deficits, resolution was observed in 34 deficits (15%), improvement in 126 deficits (54%), stability in 34 deficits (15%), and progression in 39 deficits (17%). The 12-month CNS progression-free survival was 77% among those receiving CS/WB and 51% among those receiving base of skull RT (P=.02). On multivariate analysis, patients who did not undergo stem cell transplantation after RT and base of skull RT were associated with worse CNS progression-free survival.
Conclusions: Improvement or resolution of symptoms occurred in two thirds of deficits after RT. Comprehensive radiation to the WB or CS seems to offer a better outcome, especially in isolated CNS involvement.
Crown Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Craniospinal irradiation prior to stem cell transplant for hematologic malignancies with CNS involvement: Effectiveness and toxicity after photon or proton treatment.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017 Nov-Dec;7(6):e401-e408. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 10. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28666906 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Survival and neurocognitive outcomes after cranial or craniospinal irradiation plus total-body irradiation before stem cell transplantation in pediatric leukemia patients with central nervous system involvement.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 May 1;89(1):67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.01.056. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014. PMID: 24725690
-
Role of radiation therapy to the brain in leukemic patients with cranial nerve palsies in the absence of radiological findings.Leuk Lymphoma. 1999 Feb;32(5-6):497-503. doi: 10.3109/10428199909058407. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999. PMID: 10048422 Clinical Trial.
-
Patterns of failure in relation to radiotherapy fields in supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Mar 15;58(4):1171-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.08.022. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 15001261 Review.
-
Central nervous system disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: prophylaxis and treatment.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006:142-6. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2006.1.142. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006. PMID: 17124053 Review.
Cited by
-
Craniospinal irradiation prior to stem cell transplant for hematologic malignancies with CNS involvement: Effectiveness and toxicity after photon or proton treatment.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017 Nov-Dec;7(6):e401-e408. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 10. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28666906 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Central Nervous System Involvement in Adults with Acute Leukemia: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Management.Curr Oncol Rep. 2022 Apr;24(4):427-436. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01220-4. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35141858 Review.
-
Neurological Complications of the Leukemias Across the Ages.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2017 Feb;17(2):13. doi: 10.1007/s11910-017-0726-1. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28229399 Review.
-
Central Nervous System Prophylaxis and Treatment in Acute Leukemias.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Dec;23(12):1829-1844. doi: 10.1007/s11864-022-01032-5. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36510037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Craniospinal irradiation for CNS leukemia: rates of response and durability of CNS control.J Neurooncol. 2024 Jan;166(2):351-357. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04501-5. Epub 2024 Jan 20. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 38244173
References
-
- Wellwood J, Taylor K. Central nervous system prophylaxis in haematological malignancies. Intern Med J. 2002;32:252–258. - PubMed
-
- Shihadeh F, Reed V, Faderl S, et al. Cytogenetic profile of patients with acute myeloid leukemia and central nervous system disease. Cancer. 2012;118:112–127. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S, Smith TL, et al. Results of treatment with hyper-CVAD, a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:547–561. - PubMed
-
- Omura GA, Moffitt S, Vogler WR, et al. Combination chemotherapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia with randomized central nervous system prophylaxis. Blood. 1980;55:199–204. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson G, Schmiegelow K, Forestier E, et al. Improving outcome through two decades in childhood ALL in the Nordic countries: The impact of high-dose methotrexate in the reduction of CNS irradiation. Nordic Society of Pediatric Haematology and Oncology (NOPHO) Leukemia. 2000;14:2267–2275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

