Probiotic supplementation prevents high-fat, overfeeding-induced insulin resistance in human subjects
- PMID: 25630516
- PMCID: PMC4339038
- DOI: 10.1017/S0007114514004097
Probiotic supplementation prevents high-fat, overfeeding-induced insulin resistance in human subjects
Abstract
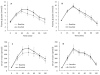
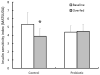
The purpose of the present study was to determine whether probiotic supplementation (Lactobacillus casei Shirota (LcS)) prevents diet-induced insulin resistance in human subjects. A total of seventeen healthy subjects were randomised to either a probiotic (n 8) or a control (n 9) group. The probiotic group consumed a LcS-fermented milk drink twice daily for 4 weeks, whereas the control group received no supplementation. Subjects maintained their normal diet for the first 3 weeks of the study, after which they consumed a high-fat (65 % of energy), high-energy (50 % increase in energy intake) diet for 7 d. Whole-body insulin sensitivity was assessed by an oral glucose tolerance test conducted before and after overfeeding. Body mass increased by 0·6 (SE 0·2) kg in the control group (P< 0·05) and by 0·3 (SE 0·2) kg in the probiotic group (P>0·05). Fasting plasma glucose concentrations increased following 7 d of overeating (control group: 5·3 (SE 0·1) v. 5·6 (SE 0·2) mmol/l before and after overfeeding, respectively, P< 0·05), whereas fasting serum insulin concentrations were maintained in both groups. Glucose AUC values increased by 10 % (from 817 (SE 45) to 899 (SE 39) mmol/l per 120 min, P< 0·05) and whole-body insulin sensitivity decreased by 27 % (from 5·3 (SE 1·4) to 3·9 (SE 0·9), P< 0·05) in the control group, whereas normal insulin sensitivity was maintained in the probiotic group (4·4 (SE 0·8) and 4·5 (SE 0·9) before and after overeating, respectively (P>0·05). These results suggest that probiotic supplementation may be useful in the prevention of diet-induced metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Probiotics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-Administration of Soluble Fibres and Lactobacillus casei NCDC19 Fermented Milk Prevents Adiposity and Insulin Resistance Via Modulation of Lipid Mobilization Genes in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug _targets. 2020;20(9):1543-1551. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666200526123621. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug _targets. 2020. PMID: 32452329
-
Effect of supplementation of fermented milk drink containing probiotic Lactobacillus casei Shirota on the concentrations of aflatoxin biomarkers among employees of Universiti Putra Malaysia: a randomised, double-blind, cross-over, placebo-controlled study.Br J Nutr. 2016 Jan 14;115(1):39-54. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515004109. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26490018 Clinical Trial.
-
Beneficial effect of oral administration of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity mice.J Appl Microbiol. 2011 Mar;110(3):650-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04922.x. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Appl Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21281408
-
Applications of probiotics.Meded Rijksuniv Gent Fak Landbouwkd Toegep Biol Wet. 2001;66(3b):557-61. Meded Rijksuniv Gent Fak Landbouwkd Toegep Biol Wet. 2001. PMID: 15954653 Review.
-
Emerging Roles of Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential.Nutr Cancer. 2019;71(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2018.1557221. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Nutr Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30686054 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex Modulates Lactobacillus johnsonii N6.2 and Phytophenol Effectiveness in Reducing High Fat Diet Induced mTOR Activation in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 6;9:2649. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02649. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30459740 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic endotoxemia with obesity: Is it real and is it relevant?Biochimie. 2016 May;124:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26133659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of macronutrients to obesity: implications for precision nutrition.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020 Jun;16(6):305-320. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0346-8. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32235875 Review.
-
Effect of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota-fermented milk on metabolic abnormalities in obese prediabetic Japanese men: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2018;37(1):9-18. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.17-012. Epub 2017 Sep 2. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2018. PMID: 29387517 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 13;17(6):928. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060928. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27304953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tremblay F, Lavigne C, Jacques H, et al. Defective insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle of high fat-fed rats is associated with alterations in both Akt/protein kinase B and atypical protein kinase C activities. Diabetes. 2001;50:1901–1910. - PubMed
-
- Defronzso RA. Dysfunctional fat cells, lipotoxicity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2004;58:9–21. - PubMed
-
- Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2007;56:1761–1772. - PubMed
-
- Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, et al. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2008;57:1470–1481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

