_targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Evasion Axis With DNA Aptamers as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for the Treatment of Disseminated Cancers
- PMID: 25919090
- PMCID: PMC4417124
- DOI: 10.1038/mtna.2015.11
_targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Evasion Axis With DNA Aptamers as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for the Treatment of Disseminated Cancers
Abstract
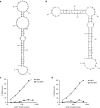
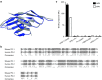
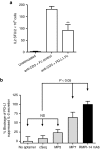
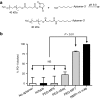
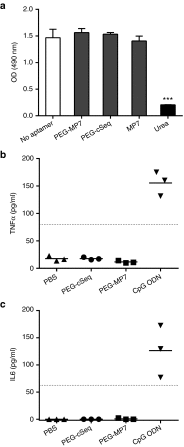
Blocking the immunoinhibitory PD-1:PD-L1 pathway using monoclonal antibodies has led to dramatic clinical responses by reversing tumor immune evasion and provoking robust and durable antitumor responses. Anti-PD-1 antibodies have now been approved for the treatment of melanoma, and are being clinically tested in a number of other tumor types as both a monotherapy and as part of combination regimens. Here, we report the development of DNA aptamers as synthetic, nonimmunogenic antibody mimics, which bind specifically to the murine extracellular domain of PD-1 and block the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction. One such aptamer, MP7, functionally inhibits the PD-L1-mediated suppression of IL-2 secretion in primary T-cells. A PEGylated form of MP7 retains the ability to block the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction, and significantly suppresses the growth of PD-L1+ colon carcinoma cells in vivo with a potency equivalent to an antagonistic anti-PD-1 antibody. Importantly, the anti-PD-1 DNA aptamer treatment was not associated with off-_target TLR-9-related immune responses. Due to the inherent advantages of aptamers including their lack of immunogenicity, low cost, long shelf life, and ease of synthesis, PD-1 antagonistic aptamers may represent an attractive alternative over antibody-based anti PD-1 therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-PD-L1 DNA aptamer antagonizes the interaction of PD-1/PD-L1 with antitumor effect.J Mater Chem B. 2021 Jan 28;9(3):746-756. doi: 10.1039/d0tb01668c. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33319876
-
A Novel PD-L1-_targeting Antagonistic DNA Aptamer With Antitumor Effects.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016 Dec 13;5(12):e397. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2016.102. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016. PMID: 27959341
-
Development and Evaluation of Novel Aptamers Specific for Human PD1 Using Hybrid Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment Approach.Immunol Invest. 2020 Jul;49(5):535-554. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2020.1744639. Epub 2020 May 19. Immunol Invest. 2020. PMID: 32429721
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions.Oncologist. 2019 Feb;24(Suppl 1):S31-S41. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-IO-S1-s05. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30819829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of selective ssDNA micro-probe for PD1 detection as a novel strategy for cancer imaging.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 19;14(1):28652. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74891-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39562585 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2024 Oct 7;29(19):4737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced SELEX Platforms for Aptamer Selection with Improved Characteristics: A Review.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 16. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01256-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39152308 Review.
-
Breaking Barriers: Nucleic Acid Aptamers in Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers Therapy.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1763-1776. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01367-w. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38916791 Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 18;23(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02023-w. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38762484 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

