Redefining ALL classification: toward detecting high-risk ALL and implementing precision medicine
- PMID: 25999453
- PMCID: PMC4481590
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-580043
Redefining ALL classification: toward detecting high-risk ALL and implementing precision medicine
Abstract
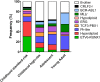
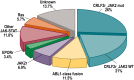
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the commonest childhood tumor and remains a leading cause of cancer death in the young. In the last decade, microarray and sequencing analysis of large ALL cohorts has revolutionized our understanding of the genetic basis of this disease. These studies have identified new ALL subtypes, each characterized by constellations of structural and sequence alterations that perturb key cellular pathways, including lymphoid development, cell-cycle regulation, and tumor suppression; cytokine receptor, kinase, and Ras signaling; and chromatin modifications. Several of these pathways, particularly kinase-activating lesions and epigenetic alterations, are logical _targets for new precision medicine therapies. Genomic profiling has also identified important interactions between inherited genetic variants that influence the risk of leukemia development and the somatic genetic alterations that are required to establish the leukemic clone. Moreover, sequential sequencing studies at diagnosis, remission, and relapse have provided important insights into the relationship among genetic variants, clonal heterogeneity, and the risk of relapse. Ongoing studies are extending our understanding of coding and noncoding genetic alterations in B-progenitor and T-lineage ALL and using these insights to inform the development of faithful experimental models to test the efficacy of new treatment approaches.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genomic characterization of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Semin Hematol. 2013 Oct;50(4):314-24. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Semin Hematol. 2013. PMID: 24246699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Basis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar 20;35(9):975-983. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7836. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28297628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomics in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: insights and treatment implications.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Jun;12(6):344-57. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.38. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25781572 Review.
-
The genomic landscape of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and precision medicine opportunities.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Sep;84:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.10.013. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33197607 Review.
-
The molecular genetic makeup of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:389-96. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.389. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012. PMID: 23233609 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of ARID5B in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Beyond.Front Genet. 2020 Jun 12;11:598. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00598. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32595701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination efficacy of ruxolitinib with standard-of-care drugs in CRLF2-rearranged Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Leukemia. 2021 Nov;35(11):3101-3112. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01248-8. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 33895784
-
In Silico Integration of Transcriptome and Interactome Predicts an ETP-ALL-Specific Transcriptional Footprint that Decodes its Developmental Propensity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 13;10:899752. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.899752. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35646901 Free PMC article.
-
A causal mechanism for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 Aug;18(8):471-484. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0015-6. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29784935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Truncating Erythropoietin Receptor Rearrangements in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2016 Feb 8;29(2):186-200. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.12.013. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 26859458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuiper RP, Schoenmakers EF, van Reijmersdal SV, et al. High-resolution genomic profiling of childhood ALL reveals novel recurrent genetic lesions affecting pathways involved in lymphocyte differentiation and cell cycle progression. Leukemia. 2007;21(6):1258–1266. - PubMed
-
- Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 2007;446(7137):758–764. - PubMed
-
- Mullighan CG, Miller CB, Radtke I, et al. BCR-ABL1 lymphoblastic leukaemia is characterized by the deletion of Ikaros. Nature. 2008;453(7191):110–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

