The effect of recombinant erythropoietin on plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in patients with affective disorders: a randomised controlled study
- PMID: 26011424
- PMCID: PMC4444304
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127629
The effect of recombinant erythropoietin on plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in patients with affective disorders: a randomised controlled study
Abstract
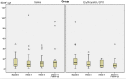
The study aims to investigate the effect of repeated infusions of recombinant erythropoietin (EPO) on plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in patients with affective disorders. In total, 83 patients were recruited: 40 currently depressed patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD) (Hamilton Depression Rating Scale-17 items (HDRS-17) score >17) (study 1) and 43 patients with bipolar disorder (BD) in partial remission (HDRS-17 and Young Mania Rating Scale (YMRS) ≤ 14) (study 2). In both studies, patients were randomised to receive eight weekly EPO (Eprex; 40,000 IU) or saline (0.9% NaCl) infusions in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel--group design. Plasma BDNF levels were measured at baseline and at weeks 5, 9 and at follow up, week 14. In contrast with our hypothesis, EPO down regulated plasma BDNF levels in patients with TRD (mean reduction at week 9 (95% CI): EPO 10.94 ng/l (4.51-21.41 ng/l); mean increase at week 9: Saline 0.52 ng/l, p=0.04 (-5.88-4.48 ng/l) p=0.04, partial ŋ2=0.12). No significant effects were found on BDNF levels in partially remitted patients with BD (p=0.35). The present effects of EPO on BDNF levels in patients with TRD point to a role of neurotrophic factors in the potential effects of EPO seen in TRD and BD. The neurobiological mechanisms underlying these effects and the interaction between EPO and peripheral levels on BDNF need to be further elucidated in human studies including a broad range of biomarkers.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT00916552.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of recombinant erythropoietin on inflammatory markers in patients with affective disorders: A randomised controlled study.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Oct;57:53-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 27181179 Clinical Trial.
-
Recombinant human erythropoietin for treating treatment-resistant depression: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 May;39(6):1399-408. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.335. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24322509 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Erythropoietin on Hippocampal Volume and Memory in Mood Disorders.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Aug 15;78(4):270-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.12.013. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25641635 Clinical Trial.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a state-marker of mood episodes in bipolar disorders: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis.J Psychiatr Res. 2011 Aug;45(8):995-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 May 6. J Psychiatr Res. 2011. PMID: 21550050 Review.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
Cited by
-
Lack of association between erythropoietin treatment and risk of depression in patients with end-stage kidney disease on maintenance dialysis: a nationwide database study in Taiwan.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021 Mar 5;12:2040622321995690. doi: 10.1177/2040622321995690. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021. PMID: 33747426 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on cognition and neural activity in remitted patients with mood disorders and first-degree relatives of patients with psychiatric disorders: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Nov 6;19(1):611. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2995-7. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30400939 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates olfactory cognitive dysfunction by promoting neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of hypoxic-ischemic neonatal rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 19;13:983920. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.983920. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36059991 Free PMC article.
-
Z-Guggulsterone Produces Antidepressant-Like Effects in Mice through Activation of the BDNF Signaling Pathway.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Jun 1;20(6):485-497. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx009. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28339691 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of erythropoietin administration on the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, stromal cell-derived Factor-1, and neuron-specific enolase in traumatic brain injury: A literature review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Aug 5;69:102666. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102666. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34429948 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chao MV, Lee FS. Neurotrophin survival signaling mechanisms. J Alzheimers Dis 2004. December;6(6 Suppl):S7–11. - PubMed
-
- Molendijk ML, Spinhoven P, Polak M, Bus BA, Penninx BW, Elzinga BM. Serum BDNF concentrations as peripheral manifestations of depression: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analyses on 179 associations (N = 9484). Mol Psychiatry 2013. August 20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous