Selective Small Molecule Induced Degradation of the BET Bromodomain Protein BRD4
- PMID: 26035625
- PMCID: PMC4548256
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00216
Selective Small Molecule Induced Degradation of the BET Bromodomain Protein BRD4
Abstract
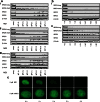
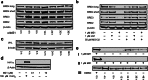
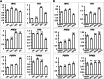
The Bromo- and Extra-Terminal (BET) proteins BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4 play important roles in transcriptional regulation, epigenetics, and cancer and are the _targets of pan-BET selective bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. However, the lack of intra-BET selectivity limits the scope of current inhibitors as probes for _target validation and could lead to unwanted side effects or toxicity in a therapeutic setting. We designed Proteolysis _targeted Chimeras (PROTACs) that tether JQ1 to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL, aimed at triggering the intracellular destruction of BET proteins. Compound MZ1 potently and rapidly induces reversible, long-lasting, and unexpectedly selective removal of BRD4 over BRD2 and BRD3. The activity of MZ1 is dependent on binding to VHL but is achieved at a sufficiently low concentration not to induce stabilization of HIF-1α. Gene expression profiles of selected cancer-related genes responsive to JQ1 reveal distinct and more limited transcriptional responses induced by MZ1, consistent with selective suppression of BRD4. Our discovery opens up new opportunities to elucidate the cellular phenotypes and therapeutic implications associated with selective _targeting of BRD4.
Figures

Comment in
-
Protein-slaying drugs could be the next blockbuster therapies.Nature. 2019 Mar;567(7748):298-300. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-00879-3. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30894734 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation.Nat Chem Biol. 2017 May;13(5):514-521. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2329. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Nat Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28288108 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel small molecule induced selective degradation of the bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain protein BRD4 and BRD2 with cellular potencies.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Jan 1;28(1):115181. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115181. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31767403
-
BRD4 PROTAC degrader MZ1 exerts anticancer effects in acute myeloid leukemia by _targeting c-Myc and ANP32B genes.Cancer Biol Ther. 2022 Dec 31;23(1):1-15. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2022.2125748. Cancer Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36170346 Free PMC article.
-
BET Bromodomain Inhibitors: Novel Design Strategies and Therapeutic Applications.Molecules. 2023 Mar 29;28(7):3043. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073043. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteolysis-_targeting chimeras mediate the degradation of bromodomain and extra-terminal domain proteins.Future Med Chem. 2020 Sep;12(18):1669-1683. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0264. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Future Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32893690 Review.
Cited by
-
A narrative review of proteolytic _targeting chimeras (PROTACs): future perspective for prostate cancer therapy.Transl Androl Urol. 2021 Feb;10(2):954-962. doi: 10.21037/tau-20-1357. Transl Androl Urol. 2021. PMID: 33718095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
_targeted Protein Degradation by Small Molecules.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Jan 6;57:107-123. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010715-103507. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27732798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Super-enhancers in esophageal carcinoma: Transcriptional addictions and therapeutic strategies.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 27;12:1036648. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1036648. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of folate receptor _targeting chimeras for cancer selective degradation of extracellular proteins.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 8;15(1):8695. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52685-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39379374 Free PMC article.
-
The peptide PROTAC modality: a novel strategy for _targeted protein ubiquitination.Theranostics. 2020 Aug 8;10(22):10141-10153. doi: 10.7150/thno.46985. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32929339 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gallenkamp D.; Gelato K. A.; Haendler B.; Weinmann H. (2014) Bromodomains and their pharmacological inhibitors. ChemMedChem. 9, 438–464. - PubMed
-
- Zuber J.; Shi J.; Wang E.; Rappaport A. R.; Herrmann H.; Sison E. A.; Magoon D.; Qi J.; Blatt K.; Wunderlich M.; Taylor M. J.; Johns C.; Chicas A.; Mulloy J. C.; Kogan S. C.; Brown P.; Valent P.; Bradner J. E.; Lowe S. W.; Vakoc C. R. (2011) RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic _target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 478, 524–528. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baratta M. G.; Schinzel A. C.; Zwang Y.; Bandopadhayay P.; Bowman-Colin C.; Kutt J.; Curtis J.; Piao H.; Wong L. C.; Kung A. L.; Beroukhim R.; Bradner J. E.; Drapkin R.; Hahn W. C.; Liu J. F.; Livingston D. M. (2015) An in-tumor genetic screen reveals that the BET bromodomain protein, BRD4, is a potential therapeutic _target in ovarian carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112, 232–237. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chung C.-W.; Coste H.; White J. H.; Mirguet O.; Wilde J.; Gosmini R. L.; Delves C.; Magny S. M.; Woodward R.; Hughes S. A.; Boursier E. V.; Flynn H.; Bouillot A. M.; Bamborough P.; Brusq J.-M. G.; Gellibert F. J.; Jones E. J.; Riou A. M.; Homes P.; Martin S. L.; Uings I. J.; Toum J.; Clément C. A.; Boullay A.-B.; Grimley R. L.; Blandel F. M.; Prinjha R. K.; Lee K.; Kirilovsky J.; Nicodeme E. (2011) Discovery and characterization of small molecule inhibitors of the BET family bromodomains. J. Med. Chem. 54, 3827–3838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

