MiRNA-1469 promotes lung cancer cells apoptosis through _targeting STAT5a
- PMID: 26045996
- PMCID: PMC4449445
MiRNA-1469 promotes lung cancer cells apoptosis through _targeting STAT5a
Abstract
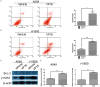
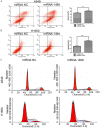
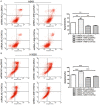
MicroRNAs play key roles in cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. In this study, we described the regulation and function of miR-1469 in apoptosis of lung cancer cells (A549 and NCI-H1650). Expression analysis verified that miR-1469 expression significantly increased in apoptotic cells. Overexpression of miR-1469 in lung cancer cells increased cell apoptosis induced by etoposide. Additionally, we identified that Stat5a is a downstream _target of miR-1469, which can bind directly to the 3'-untranslated region of the Stat5a, subsequently reducing both the mRNA and protein levels of Stat5a. Finally, co-expression of miR-1469 and Stat5a in A549 and NCI-H1650 cells partially abrogated the effect of miR-1469 on cell apoptosis. Our results show that miR-1469 functions as an apoptosis enhancer to regulate lung cancer apoptosis through _targeting Stat5a and may become a critical therapeutic _target in lung cancer.
Keywords: MicroRNA; Stat5a; apoptosis; lung cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-125a-5p plays a role as a tumor suppressor in lung carcinoma cells by directly _targeting STAT3.Tumour Biol. 2017 Jun;39(6):1010428317697579. doi: 10.1177/1010428317697579. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28631574
-
The novel microRNA hsa-miR-CHA1 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in human lung cancer by _targeting XIAP.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jun;132:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31097102
-
MicroRNA-221 regulates proliferation of bovine mammary gland epithelial cells by _targeting the STAT5a and IRS1 genes.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Jan;102(1):426-435. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15108. Epub 2018 Oct 23. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30366615
-
MicroRNA-641 inhibits lung cancer cells proliferation, metastasis but promotes apoptosis in cells by _targeting PDCD4.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Aug 1;10(8):8211-8221. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966672 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-26a Contributes to the Acquisition of Malignant Behaviors of Doctaxel-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells through _targeting EZH2.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(2):583-597. doi: 10.1159/000457879. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28214878
Cited by
-
Identification of high expression profiles of miR-31-5p and its vital role in lung squamous cell carcinoma: a survey based on qRT-PCR and bioinformatics analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Jun;8(3):788-801. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.04.21. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116817 Free PMC article.
-
Current state of phenolic and terpenoidal dietary factors and natural products as non-coding RNA/microRNA modulators for improved cancer therapy and prevention.Noncoding RNA Res. 2016 Jul 27;1(1):12-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2016.07.001. eCollection 2016 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2016. PMID: 30159408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LPS induces HUVEC angiogenesis in vitro through miR-146a-mediated TGF-β1 inhibition.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Feb 15;9(2):591-600. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28337286 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term exposure of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to ethanol stimulates oncogenic features.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jan;50(1):49-65. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3800. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27959387 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5a Confers Doxorubicin Resistance to Breast Cancer by Regulating ABCB1.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 15;11:697950. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.697950. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34336684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Pirozynski M. 100 years of lung cancer. Respir Med. 2006;100:2073–2084. - PubMed
-
- Harmsma M, Schutte B, Ramaekers FC. Serum markers in small cell lung cancer: opportunities for improvement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1836:255–272. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
