Ultrastructural evidence for synaptic contacts between cortical noradrenergic afferents and endocannabinoid-synthesizing post-synaptic neurons
- PMID: 26162236
- PMCID: PMC4542008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.009
Ultrastructural evidence for synaptic contacts between cortical noradrenergic afferents and endocannabinoid-synthesizing post-synaptic neurons
Abstract
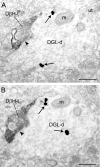
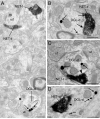
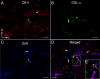
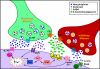
Endocannabinoids (eCBs) are involved in a myriad of physiological processes that are mediated through the activation of cannabinoid receptors, which are ubiquitously distributed within the nervous system. One neurochemical _target at which cannabinoids interact to have global effects on behavior is brain noradrenergic circuitry. We, and others, have previously shown that CB type 1 receptors (CB1r) are positioned to pre-synaptically modulate norepinephrine (NE) release in the rat frontal cortex (FC). Diacylglycerol lipase (DGL) is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). While DGL-α is expressed in the FC in the rat brain, it is not known whether noradrenergic afferents _target neurons expressing synthesizing enzymes for the endocannabinoid, 2-AG. In the present study, we employed high-resolution neuroanatomical approaches to better define cellular sites for interactions between noradrenergic afferents and FC neurons expressing DGL-α. Immunofluorescence microscopy showed close appositions between processes containing the norepinephrine transporter (NET) or dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DβH) and cortical neurons expressing DGL-α-immunoreactivity. Ultrastructural analysis using immunogold-silver labeling for DGL-α and immunoperoxidase labeling for NET or DβH confirmed that NET-labeled axon terminals were directly apposed to FC somata and dendritic processes that exhibited DGL-α-immunoreactivity. Finally, tissue sections were processed for immunohistochemical detection of DGL-α, CB1r and DβH. Triple label immunofluorescence revealed that CB1r and DβH were co-localized in common cellular profiles and these were in close association with DGL-α. Taken together, these data provide anatomical evidence for direct synaptic associations between noradrenergic afferents and cortical neurons exhibiting endocannabinoid synthesizing machinery.
Keywords: cannabinoid receptor type 1; diacylglycerol lipase; dopamine-β-hydroxylase; electron microscopy; norepinephrine transporter.
Copyright © 2015 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular architecture of endocannabinoid signaling at nociceptive synapses mediating analgesia.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 May;29(10):1964-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06751.x. Epub 2009 May 9. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19453631 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid receptors are localized to noradrenergic axon terminals in the rat frontal cortex.Brain Res. 2007 Jan 5;1127(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.09.110. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17113043 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptors and diacylglycerol lipase-α initiates 2-arachidonoylglycerol formation and endocannabinoid-mediated analgesia.J Neurosci. 2012 Jul 11;32(28):9457-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0013-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22787031 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing local effects of endocannabinoids on the activity of noradrenergic neurons and release of noradrenaline: relevance for their role in depression and in the actions of CB(1) receptor antagonists.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013 Jan;120(1):177-86. doi: 10.1007/s00702-012-0900-1. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013. PMID: 22990678 Review.
-
Cholinergic axon terminals in the ventral tegmental area _target a subpopulation of neurons expressing low levels of the dopamine transporter.J Comp Neurol. 1999 Jul 26;410(2):197-210. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990726)410:2<197::aid-cne3>3.0.co;2-d. J Comp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10414527 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in the effect of cannabinoid type 1 receptor deletion on locus coeruleus-norepinephrine neurons and corticotropin releasing factor-mediated responses.Eur J Neurosci. 2018 Sep;48(5):2118-2138. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14103. Eur J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30103253 Free PMC article.
-
_targeting the cannabinoid system to counteract the deleterious effects of stress in Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 4;14:949361. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.949361. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36268196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noradrenergic depletion causes sex specific alterations in the endocannabinoid system in the Murine prefrontal cortex.Neurobiol Stress. 2019 Apr 10;10:100164. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2019.100164. eCollection 2019 Feb. Neurobiol Stress. 2019. PMID: 31193575 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical adrenoceptor expression, function and adaptation under conditions of cannabinoid receptor deletion.Exp Neurol. 2017 Jun;292:179-192. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Exp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28341460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnsten AF. Catecholamine and second messenger influences on prefrontal cortical networks of “representational knowledge”: a rational bridge between genetics and the symptoms of mental illness. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17(Suppl 1):i6–i15. - PubMed
-
- Berridge CW, Waterhouse BD. The locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system: modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res Brain Rev. 2003;42:33–84. - PubMed
-
- Bisogno T, Di Marzo V. Cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids: role in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders. CNS Neurol Disord Drug _targets. 2010;9:564–573. - PubMed
-
- Bisogno T, Howell F, Williams G, Minassi A, Cascio MG, Ligresti A, Matias I, Schiano-Moriello A, Paul P, Williams EJ, Gangadharan U, Hobbs C, Di Marzo V, Doherty P. Cloning of the first sn1-DAG lipases points to the spatial and temporal regulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. J Cell Biol. 2003;163:463–468. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

