Hippocampal Insulin Resistance Impairs Spatial Learning and Synaptic Plasticity
- PMID: 26216852
- PMCID: PMC4613975
- DOI: 10.2337/db15-0596
Hippocampal Insulin Resistance Impairs Spatial Learning and Synaptic Plasticity
Abstract
Insulin receptors (IRs) are expressed in discrete neuronal populations in the central nervous system, including the hippocampus. To elucidate the functional role of hippocampal IRs independent of metabolic function, we generated a model of hippocampal-specific insulin resistance using a lentiviral vector expressing an IR antisense sequence (LV-IRAS). LV-IRAS effectively downregulates IR expression in the rat hippocampus without affecting body weight, adiposity, or peripheral glucose homeostasis. Nevertheless, hippocampal neuroplasticity was impaired in LV-IRAS-treated rats. High-frequency stimulation, which evoked robust long-term potentiation (LTP) in brain slices from LV control rats, failed to evoke LTP in LV-IRAS-treated rats. GluN2B subunit levels, as well as the basal level of phosphorylation of GluA1, were reduced in the hippocampus of LV-IRAS rats. Moreover, these deficits in synaptic transmission were associated with impairments in spatial learning. We suggest that alterations in the expression and phosphorylation of glutamate receptor subunits underlie the alterations in LTP and that these changes are responsible for the impairment in hippocampal-dependent learning. Importantly, these learning deficits are strikingly similar to the impairments in complex task performance observed in patients with diabetes, which strengthens the hypothesis that hippocampal insulin resistance is a key mediator of cognitive deficits independent of glycemic control.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures
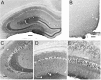
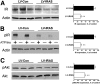
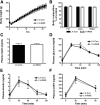
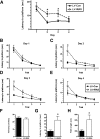

Comment in
-
A Key Role of Insulin Receptors in Memory.Diabetes. 2015 Nov;64(11):3653-5. doi: 10.2337/dbi15-0011. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26494219 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Obesity/hyperleptinemic phenotype adversely affects hippocampal plasticity: effects of dietary restriction.Physiol Behav. 2011 Aug 3;104(2):235-41. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.10.020. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21036186 Free PMC article.
-
Lentivirus-mediated downregulation of hypothalamic insulin receptor expression.Physiol Behav. 2007 Nov 23;92(4):691-701. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.05.043. Epub 2007 May 21. Physiol Behav. 2007. PMID: 17585961 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of morphine decreases CREBSerine-133 phosphorylation and synaptic plasticity range mediated by glutamatergic transmission in the hippocampal CA1 area of cognitive-deficient rat offspring.Hippocampus. 2003;13(8):915-21. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10137. Hippocampus. 2003. PMID: 14750654
-
Minireview: Food for thought: regulation of synaptic function by metabolic hormones.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jan;29(1):3-13. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1328. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25470238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin resistance and hippocampal dysfunction: Disentangling peripheral and brain causes from consequences.Exp Neurol. 2019 Aug;318:71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31028829 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of metabolic stress and metformin on synaptic protein profile in SH-SY5Y-derived neurons.Physiol Rep. 2023 Nov;11(22):10.14814/phy2.15852. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15852. Physiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 38010200 Free PMC article.
-
Affective and Cognitive Impairments in Rodent Models of Diabetes.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(8):1327-1343. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240124164804. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38279738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for preserved insulin responsiveness in the aging rat brain.Geroscience. 2022 Oct;44(5):2491-2508. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00618-z. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Geroscience. 2022. PMID: 35798912 Free PMC article.
-
Research landscape and emerging trends of diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jul 28;17:1214301. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1214301. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37575299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of the Science on Brain Insulin Resistance and Cognitive Decline Due to Alzheimer's Disease.Aging Dis. 2024 Aug 1;15(4):1688-1725. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0814. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37611907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doré S, Kar S, Rowe W, Quirion R. Distribution and levels of [125I]IGF-I, [125I]IGF-II and [125I]insulin receptor binding sites in the hippocampus of aged memory-unimpaired and -impaired rats. Neuroscience 1997;80:1033–1040 - PubMed
-
- Park CR. Cognitive effects of insulin in the central nervous system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2001;25:311–323 - PubMed
-
- Gold SM, Dziobek I, Sweat V, et al. . Hippocampal damage and memory impairments as possible early brain complications of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007;50:711–719 - PubMed
-
- Manschot SM, Brands AM, van der Grond J, et al. .; Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy Study Group . Brain magnetic resonance imaging correlates of impaired cognition in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006;55:1106–1113 - PubMed
-
- Benedict C, Hallschmid M, Schultes B, Born J, Kern W. Intranasal insulin to improve memory function in humans. Neuroendocrinology 2007;86:136–142 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

