Soluble CD40 Ligand in Aspirin-Treated Patients Undergoing Cardiac Catheterization
- PMID: 26237513
- PMCID: PMC4523196
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134599
Soluble CD40 Ligand in Aspirin-Treated Patients Undergoing Cardiac Catheterization
Abstract
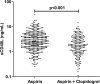
Plasma soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L) is mainly generated by cleavage of CD40L from the surface of activated platelets, and therefore considered a platelet activation marker. Although the predictive value of sCD40L for ischemic events has been demonstrated in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), studies on the association of sCD40L with cardiovascular outcomes in lower risk populations yielded heterogeneous results. We therefore sought to investigate factors influencing sCD40L levels, and the predictive value of sCD40L for long-term ischemic events in unselected, aspirin-treated patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. sCD40L was determined by a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 682 consecutive patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. Two-year follow-up data were obtained from 562 patients. Dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel was associated with significantly lower levels of sCD40L and lower platelet surface expressions of P-selectin and activated GPIIb/IIIa compared to aspirin monotherapy (all p≤0.01). Hypertension was linked to lower plasma concentrations of sCD40L, whereas female sex, increasing high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and hematocrit were associated with higher sCD40L concentrations (all p<0.05). sCD40L levels were similar in patients without and with the primary endpoint in the overall study population (p = 0.4). Likewise, sCD40L levels did not differ significantly between patients without and with the secondary endpoints (both p≥0.4). Similar results were obtained when only patients with angiographically-proven coronary artery disease (n = 459), stent implantation (n = 205) or ACS (n = 125) were analyzed. The adjustment for differences in patient characteristics by multivariate regression analyses did not change the results. ROC curve analyses did not reveal cut-off values for sCD40L for the prediction of the primary or secondary endpoints. In conclusion, plasma sCD40L levels are reduced by antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel, but not associated with long-term ischemic outcomes in unselected consecutive aspirin-treated patients undergoing cardiac catheterization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomized comparison of the effects of ASA plus clopidogrel versus ASA alone on early platelet activation in acute coronary syndromes with elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and soluble CD40 ligand levels.Clin Ther. 2006 Jun;28(6):860-71. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.06.010. Clin Ther. 2006. PMID: 16860169 Clinical Trial.
-
CD40 ligand: a novel _target in the fight against cardiovascular disease.Ann Pharmacother. 2004 Sep;38(9):1500-8. doi: 10.1345/aph.1D611. Epub 2004 Jul 27. Ann Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15280513 Review.
-
In Vivo and protease-activated receptor-1-mediated platelet activation in patients presenting for cardiac catheterization.Platelets. 2016 Jun;27(4):308-16. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2015.1095876. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Platelets. 2016. PMID: 26556638
-
Men with lower HDL cholesterol levels have significant increment of soluble CD40 ligand and high-sensitivity CRP levels following the cessation of long-term clopidogrel therapy.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2015;22(3):284-92. doi: 10.5551/jat.26765. Epub 2014 Oct 1. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2015. PMID: 25273829
-
Antiplatelet intervention in acute coronary syndrome.Am J Ther. 2009 Sep-Oct;16(5):e29-40. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31804c7238. Am J Ther. 2009. PMID: 19092648 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of antiplatelet agents on Escherichia coli sepsis mechanisms: A review.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 9;13:1043334. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1043334. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36569083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of sCD40L in the prediction of super-response to cardiac resynchronization therapy.An Sist Sanit Navar. 2021 Aug 20;44(2):205-214. doi: 10.23938/ASSN.0947. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2021. PMID: 34132247 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Platelet Release Factors as Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 21;8:684920. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.684920. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34235190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum sCD40L and IL-31 in Association with Early Phase of IgA Nephropathy.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 3;12(5):2023. doi: 10.3390/jcm12052023. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902810 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of CYP2C19 Variants on Clinical Efficacy of Clopidogrel and 1-Year Clinical Outcomes in Coronary Heart Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 24;7:453. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00453. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27932982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ruggeri ZM. Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nat Med. 2002;8: 1227–1234. - PubMed
-
- Henn V, Steinbach S, Buchner K, Presek P, Kroczek RA. The inflammatory action of CD40 ligand (CD154) expressed on activated human platelets is temporally limited by coexpressed CD40. Blood. 2001;98: 1047–1054. - PubMed
-
- Nannizzi-Alaimo L, Rubenstein MH, Alves VL, Leong GY, Phillips DR, Gold HK. Cardiopulmonary bypass induces release of soluble CD40 ligand. Circulation. 2002;105: 2849–2854. - PubMed
-
- Andre P, Nannizzi-Alaimo L, Prasad SK, Phillips DR. Platelet-derived CD40L: the switch-hitting player of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2002;106: 896–899. - PubMed
-
- Varo N, Vicent D, Libby P, Nuzzo R, Calle-Pascual AL, Bernal MR, et al. Elevated plasma levels of the atherogenic mediator soluble CD40 ligand in diabetic patients: a novel _target of thiazolidinediones. Circulation. 2003;107: 2664–2669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials