Novel iodoacetamido benzoheterocyclic derivatives with potent antileukemic activity are inhibitors of STAT5 phosphorylation
- PMID: 26629859
- PMCID: PMC4724257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.11.022
Novel iodoacetamido benzoheterocyclic derivatives with potent antileukemic activity are inhibitors of STAT5 phosphorylation
Abstract
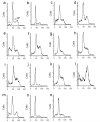
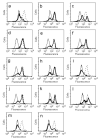
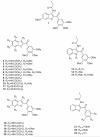
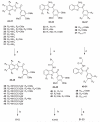
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5 (STAT5) protein, a component of the STAT family of signaling proteins, is considered to be an attractive therapeutic _target because of its involvement in the progression of acute myeloid leukemia. In an effort to discover potent molecules able to inhibit the phosphorylation-activation of STAT5, twenty-two compounds were synthesized and evaluated on the basis of our knowledge of the activity of 2-(3',4',5'-trimethoxybenzoyl)-3-iodoacetamido-6-methoxy benzo[b]furan derivative 1 as a potent STAT5 inhibitor. Most of these molecules, structurally related to compound 1, were characterized by the presence of a common 3',4',5'-trimethoxybenzoyl moiety at the 2-position of different benzoheterocycles such as benzo[b]furan, benzo[b]thiophene, indole and N-methylindole. Effects on biological activity of the iodoacetamido group and of different moieties (methyl and methoxy) at the C-3 to C-7 positions were examined. In the series of benzo[b]furan derivatives, moving the iodoacetylamino group from the C-4 to the C-5 or C-6 positions did not significantly affect antiproliferative activity. Compounds 4, 15, 20 and 23 blocked STAT5 signals and induced apoptosis of K562 BCR-ABL positive cells. For compound 23, the trimethoxybenzoyl moiety at the 2-position of the benzo[b]furan core was not essential for potent inhibition of STAT5 activation.
Keywords: Apoptosis; BCR/ABL expressing leukemia; In vitro antiproliferative activity; STAT5 inhibitors; Structure-activity relationship.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Pimozide Derivatives on pSTAT5 in K562 Cells.ChemMedChem. 2017 Aug 8;12(15):1183-1190. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201700234. Epub 2017 Jul 19. ChemMedChem. 2017. PMID: 28657677
-
The new iodoacetamidobenzofuran derivative TR120 decreases STAT5 expression and induces antitumor effects in imatinib-sensitive and imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL-expressing leukemia cells.Anticancer Drugs. 2013 Apr;24(4):384-93. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32835e64a0. Anticancer Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23370613
-
New Inhibitor _targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5 (STAT5) Signaling in Myeloid Leukemias.J Med Chem. 2017 Jul 27;60(14):6119-6136. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00369. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28654259
-
Synthesis and antitumor molecular mechanism of agents based on amino 2-(3',4',5'-trimethoxybenzoyl)benzo[b]furan: inhibition of tubulin and induction of apoptosis.ChemMedChem. 2011 Oct 4;6(10):1841-53. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100279. Epub 2011 Aug 1. ChemMedChem. 2011. PMID: 21805646 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5: From Pathogenesis Mechanism to Therapeutic Approach in Acute Leukemia.Lab Med. 2020 Jul 8;51(4):345-351. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmz074. Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 31860086 Review.
Cited by
-
The Progress of Small Molecule _targeting BCR-ABL in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(6):642-663. doi: 10.2174/0113895575218335230926070130. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37855278 Review.
-
Nanoparticles _targeting STATs in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2019 Sep 27;8(10):1158. doi: 10.3390/cells8101158. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31569687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct _targeting Options for STAT3 and STAT5 in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 3;11(12):1930. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121930. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817042 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM, Lydon NB, Kantarjian H, Capdeville R, Ohno-Jones S, Sawyers CL. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 344(2001):1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Quintas-Cardama A, Kantarjian H, Cortes J. Flying under the radar: the new wave of BCR-ABL inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:834–848. - PubMed
-
- Tolomeo M, Dieli F, Gebbia N, Simoni D. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009;9:853–863. - PubMed
-
- Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN, Sawyers CL. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science. 2001;293:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Settleman J. Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors during cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008;18:73–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

