MicroRNA-27b Regulates Mitochondria Biogenesis in Myocytes
- PMID: 26849429
- PMCID: PMC4746119
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148532
MicroRNA-27b Regulates Mitochondria Biogenesis in Myocytes
Abstract
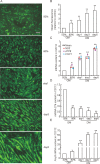
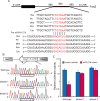
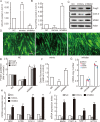
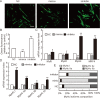
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that affect the post-transcriptional regulation of various biological pathways. To date, it is not fully understood how miRNAs regulate mitochondrial biogenesis. This study aimed at the identification of the role of miRNA-27b in mitochondria biogenesis. The mitochondria content in C2C12 cells was significantly increased during myogenic differentiation and accompanied by a marked decrease of miRNA-27b expression. Furthermore, the expression of the predicted _target gene of miRNA-27b, forkhead box j3 (Foxj3), was also increased during myogenic differentiation. Luciferase activity assays confirmed that miRNA-27b directly _targets the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of Foxj3. Overexpression of miRNA-27b provoked a decrease of mitochondria content and diminished expression of related mitochondrial genes and Foxj3 both at mRNA and protein levels. The expression levels of downstream genes of Foxj3, such as Mef2c, PGC1α, NRF1 and mtTFA, were also decreased in C2C12 cells upon overexpression of miRNA-27b. These results suggested that miRNA-27b may affect mitochondria biogenesis by down-regulation of Foxj3 during myocyte differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-494 regulates mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle through mitochondrial transcription factor A and Forkhead box j3.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Dec 15;303(12):E1419-27. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00097.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 23047984
-
MicroRNA-23a reduces slow myosin heavy chain isoforms composition through myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C) and potentially influences meat quality.Meat Sci. 2016 Jun;116:201-6. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.02.023. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Meat Sci. 2016. PMID: 26897085
-
MicroRNA-761 regulates mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse skeletal muscle in response to exercise.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Nov 6;467(1):103-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.09.113. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26408907
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Translational regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Dec 15;44(6):1717-1724. doi: 10.1042/BST20160071C. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27913682 Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise, redox homeostasis and the epigenetic landscape.Redox Biol. 2020 Aug;35:101477. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101477. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32127290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk Between miRNA and Protein Expression Profiles in Nitrate-Exposed Brain Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jul;60(7):3855-3872. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03316-9. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36971918
-
An unbiased silencing screen in muscle cells identifies miR-320a, miR-150, miR-196b, and miR-34c as regulators of skeletal muscle mitochondrial metabolism.Mol Metab. 2017 Nov;6(11):1429-1442. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29107290 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-27a/FOXJ3 Axis Dysregulates Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 5;13(19):4994. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194994. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638478 Free PMC article.
-
miR-425-5p, a SOX2 _target, regulates the expression of FOXJ3 and RAB31 and promotes the survival of GSCs.Arch Clin Biomed Res. 2020;4(3):221-238. doi: 10.26502/acbr.50170100. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Arch Clin Biomed Res. 2020. PMID: 32905473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kelly DP, Scarpulla RC. Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Gene Dev. 2004;18(4):357–68. - PubMed
-
- Menshikova EV, Ritov VB, Toledo FG, Ferrell RE, Goodpaster BH, Kelley DE. Effects of weight loss and physical activity on skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in obesity. Am J Physiol-Endoc M. 2005;288(4):E818–E25. - PubMed
-
- Russell AP, Foletta VC, Snow RJ, Wadley GD. Skeletal muscle mitochondria: a major player in exercise, health and disease. BBA-Gen Subjects. 2014;1840(4):1276–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

