Mitochondria in lung disease
- PMID: 26928034
- PMCID: PMC4767339
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI81113
Mitochondria in lung disease
Abstract
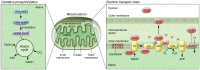
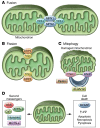
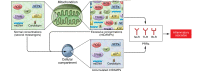
Mitochondria are a distinguishing feature of eukaryotic cells. Best known for their critical function in energy production via oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), mitochondria are essential for nutrient and oxygen sensing and for the regulation of critical cellular processes, including cell death and inflammation. Such diverse functional roles for organelles that were once thought to be simple may be attributed to their distinct heteroplasmic genome, exclusive maternal lineage of inheritance, and ability to generate signals to communicate with other cellular organelles. Mitochondria are now thought of as one of the cell's most sophisticated and dynamic responsive sensing systems. Specific signatures of mitochondrial dysfunction that are associated with disease pathogenesis and/or progression are becoming increasingly important. In particular, the centrality of mitochondria in the pathological processes and clinical phenotypes associated with a range of lung diseases is emerging. Understanding the molecular mechanisms regulating the mitochondrial processes of lung cells will help to better define phenotypes and clinical manifestations associated with respiratory disease and to identify potential diagnostic and therapeutic _targets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Lung Pathogenesis.Annu Rev Physiol. 2017 Feb 10;79:495-515. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034322. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27959621 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammatory responses and cellular senescence: pathogenesis and pharmacological _targets for chronic lung diseases.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;173(15):2305-18. doi: 10.1111/bph.13518. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27189175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of compartmentalized signaling pathways in the control of mitochondrial activities in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018 Apr;1869(2):293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29673970 Review.
-
Exercise-Induced Mitochondrial Adaptations in Addressing Heart Failure.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:323-332. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4304-8_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29098628
-
The Emerging Role of MitomiRs in the Pathophysiology of Human Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:123-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663182
Cited by
-
Effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): Current understanding and future perspectives.J Leukoc Biol. 2021 Jul;110(1):27-38. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MR0321-545RR. Epub 2021 May 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33955590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botanical formulation HX110B ameliorates PPE-induced emphysema in mice via regulation of PPAR/RXR signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 25;19(7):e0305911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305911. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39052574 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in lung ageing and disease.Eur Respir Rev. 2020 Oct 15;29(157):200165. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0165-2020. Print 2020 Sep 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2020. PMID: 33060165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breath of Fresh Air: Toward Unraveling the Molecular Underpinnings of Sleep Apnea.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Dec 15;206(12):1450-1451. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202207-1410ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35944212 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MTMR14 Alleviates Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Regulator in Inflammation and Emphysema.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 7;2022:9300269. doi: 10.1155/2022/9300269. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35035670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Respiratory Society . European Lung White Book. Yorkshire, United Kingdom: European Respiratory Society; 2013.
-
- Natarajan V, Parinandi NL. Mitochondrial Function In Lung Health And Disease. New York, New York, USA: Humana Press; 2014.
-
- Williamson JR, Corkey BE. Assay of citric acid cycle intermediates and related compounds — update with tissue metabolite levels and intracellular distribution. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:200–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R00 HL125899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL079904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL055330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P0-HL105339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL105339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99HL125899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL125899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

