Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes
- PMID: 27029739
- PMCID: PMC4821875
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11089
Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes
Abstract
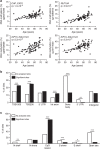
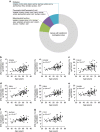
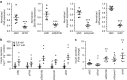
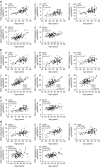
Aging associates with impaired pancreatic islet function and increased type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk. Here we examine whether age-related epigenetic changes affect human islet function and if blood-based epigenetic biomarkers reflect these changes and associate with future T2D. We analyse DNA methylation genome-wide in islets from 87 non-diabetic donors, aged 26-74 years. Aging associates with increased DNA methylation of 241 sites. These sites cover loci previously associated with T2D, for example, KLF14. Blood-based epigenetic biomarkers reflect age-related methylation changes in 83 genes identified in human islets (for example, KLF14, FHL2, ZNF518B and FAM123C) and some associate with insulin secretion and T2D. DNA methylation correlates with islet expression of multiple genes, including FHL2, ZNF518B, GNPNAT1 and HLTF. Silencing these genes in β-cells alter insulin secretion. Together, we demonstrate that blood-based epigenetic biomarkers reflect age-related DNA methylation changes in human islets, and associate with insulin secretion in vivo and T2D.
Figures

Comment in
-
Epigenetics: Blood-based markers for T2DM.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016 Jun;12(6):311. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.63. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27109784 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing of Human Pancreatic Islets Reveals Novel Differentially Methylated Regions in Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis.Diabetes. 2017 Apr;66(4):1074-1085. doi: 10.2337/db16-0996. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28052964
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of human pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic donors identifies candidate genes that influence insulin secretion.PLoS Genet. 2014 Mar 6;10(3):e1004160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004160. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24603685 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of palmitate on genome-wide mRNA expression and DNA methylation patterns in human pancreatic islets.BMC Med. 2014 Jun 23;12:103. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-12-103. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 24953961 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of insulin action and secretion - role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.J Intern Med. 2020 Aug;288(2):158-167. doi: 10.1111/joim.13049. Epub 2020 May 3. J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32363639 Review.
-
Does epigenetic dysregulation of pancreatic islets contribute to impaired insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes?Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;93(5):511-21. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2015-0057. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26369706 Review.
Cited by
-
INGAP-Peptide Variants as a Novel Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Effect on Human Islet Insulin Secretion and Gene Expression.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 31;14(9):1833. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091833. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145580 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis of Brain DNA Methylation Across Sex, Age, and Alzheimer's Disease Points for Accelerated Epigenetic Aging in Neurodegeneration.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Mar 11;13:639428. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.639428. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33790779 Free PMC article.
-
recountmethylation enables flexible analysis of public blood DNA methylation array data.Bioinform Adv. 2023 Feb 20;3(1):vbad020. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbad020. eCollection 2023. Bioinform Adv. 2023. PMID: 36874953 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Factors, DNA Methylation, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: Perspectives and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 19;20(12):2983. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122983. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31248068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and Type 2 Diabetes Risk.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Jun 27;19(8):47. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1168-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31250127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chang A. M. & Halter J. B. Aging and insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 284, E7–12 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

