New Hippocampal Neurons Mature Rapidly in Response to Ketamine But Are Not Required for Its Acute Antidepressant Effects on Neophagia in Rats
- PMID: 27066531
- PMCID: PMC4819285
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0116-15.2016
New Hippocampal Neurons Mature Rapidly in Response to Ketamine But Are Not Required for Its Acute Antidepressant Effects on Neophagia in Rats
Abstract
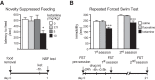
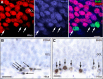
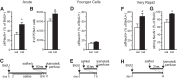
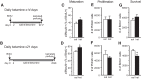
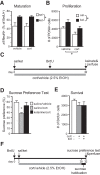
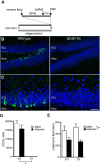
Virtually all antidepressant agents increase the birth of granule neurons in the adult dentate gyrus in rodents, providing a key basis for the neurogenesis hypothesis of antidepressant action. The novel antidepressant ketamine, however, shows antidepressant activity in humans within hours, far too rapid for a mechanism involving neuronal birth. Ketamine could potentially act more rapidly by enhancing maturation of new neurons born weeks earlier. To test this possibility, we assessed the effects of S-ketamine (S-(+)-ketamine hydrochloride) injection on maturation, as well as birth and survival, of new dentate gyrus granule neurons in rats, using the immediate-early gene zif268, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and BrdU, respectively. We show that S-ketamine has rapid effects on new neurons, increasing the proportion of functionally mature young granule neurons within 2 h. A single injection of S-ketamine also increased cell proliferation and functional maturation, and decreased depressive-like behavior, for at least 4 weeks in rats treated with long-term corticosterone administration (a depression model) and controls. However, the behavioral effects of S-ketamine on neophagia were unaffected by elimination of adult neurogenesis. Together, these results indicate that ketamine has surprisingly rapid and long-lasting effects on the recruitment of young neurons into hippocampal networks, but that ketamine has antidepressant-like effects that are independent of adult neurogenesis.
Keywords: antidepressive agents; cell proliferation; dentate gyrus; mood disorders; neurogenesis; neuronal maturation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippocampal VEGF is necessary for antidepressant-like behaviors but not sufficient for antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in rats.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jul;1862(7):1247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27063455
-
Imipramine protects against the deleterious effects of chronic corticosterone on depression-like behavior, hippocampal reelin expression, and neuronal maturation.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Jul 3;60:52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25681757
-
Blockade of the GABA(B) receptor increases neurogenesis in the ventral but not dorsal adult hippocampus: relevance to antidepressant action.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Dec;63(8):1380-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.066. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22884610
-
Implications of the functional integration of adult-born hippocampal neurons in anxiety-depression disorders.Neuroscientist. 2010 Oct;16(5):578-91. doi: 10.1177/1073858409360281. Neuroscientist. 2010. PMID: 20889967 Review.
-
Signaling pathways underlying the rapid antidepressant actions of ketamine.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Jan;62(1):35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.08.044. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21907221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ketamine Alters Hippocampal Cell Proliferation and Improves Learning in Mice after Traumatic Brain Injury.Anesthesiology. 2018 Aug;129(2):278-295. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002197. Anesthesiology. 2018. PMID: 29734230 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenesis affects motivation to obtain weak, but not strong, reward in operant tasks.Hippocampus. 2018 Jul;28(7):512-522. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22950. Epub 2018 May 4. Hippocampus. 2018. PMID: 29663595 Free PMC article.
-
JNK Regulation of Depression and Anxiety.Brain Plast. 2018 Aug 10;3(2):145-155. doi: 10.3233/BPL-170062. Brain Plast. 2018. PMID: 30151339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketamine's rapid and sustained antidepressant effects are driven by distinct mechanisms.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Feb 27;81(1):105. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05121-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38413417 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrative Approach to Ketamine Therapy May Enhance Multiple Dimensions of Efficacy: Improving Therapeutic Outcomes With Treatment Resistant Depression.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 24;12:710338. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.710338. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34899408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodnoff SR, Suranyi-Cadotte B, Aitken DH, Quirion R, Meaney MJ (1988) The effects of chronic antidepressant treatment in an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 95:298–302. - PubMed
-
- Brachman RA, McGowan JC, Perusini JN, Lim SC, Pham TH, Faye C, Gardier AM, Mendez-David I, David DJ, Hen R, Denny CA (2015) Ketamine as a prophylactic against stress-induced depressive-like behavior. Biol Psychiatry. Advance online publication. Retrieved March 23, 2016. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.04.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
