Quercetin, a Natural Flavonoid Interacts with DNA, Arrests Cell Cycle and Causes Tumor Regression by Activating Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis
- PMID: 27068577
- PMCID: PMC4828642
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24049
Quercetin, a Natural Flavonoid Interacts with DNA, Arrests Cell Cycle and Causes Tumor Regression by Activating Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis
Abstract
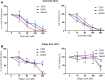
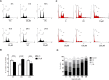
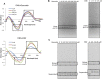
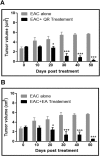
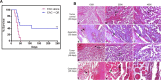
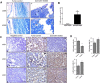
Naturally occurring compounds are considered as attractive candidates for cancer treatment and prevention. Quercetin and ellagic acid are naturally occurring flavonoids abundantly seen in several fruits and vegetables. In the present study, we evaluate and compare antitumor efficacies of quercetin and ellagic acid in animal models and cancer cell lines in a comprehensive manner. We found that quercetin induced cytotoxicity in leukemic cells in a dose-dependent manner, while ellagic acid showed only limited toxicity. Besides leukemic cells, quercetin also induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells, however, its effect on normal cells was limited or none. Further, quercetin caused S phase arrest during cell cycle progression in tested cancer cells. Quercetin induced tumor regression in mice at a concentration 3-fold lower than ellagic acid. Importantly, administration of quercetin lead to ~5 fold increase in the life span in tumor bearing mice compared to that of untreated controls. Further, we found that quercetin interacts with DNA directly, and could be one of the mechanisms for inducing apoptosis in both, cancer cell lines and tumor tissues by activating the intrinsic pathway. Thus, our data suggests that quercetin can be further explored for its potential to be used in cancer therapeutics and combination therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low concentrations of quercetin and ellagic acid synergistically influence proliferation, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in MOLT-4 human leukemia cells.J Nutr. 2003 Aug;133(8):2669-74. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.8.2669. J Nutr. 2003. PMID: 12888656
-
Ellagic acid and quercetin interact synergistically with resveratrol in the induction of apoptosis and cause transient cell cycle arrest in human leukemia cells.Cancer Lett. 2005 Feb 10;218(2):141-51. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.06.007. Cancer Lett. 2005. PMID: 15670891
-
Quercetin-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis involving activation of a caspase cascade through the mitochondrial pathway in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Aug;33(8):1181-91. doi: 10.1007/s12272-010-0808-y. Epub 2010 Aug 28. Arch Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 20803121
-
Quercetin and the mitochondria: A mechanistic view.Biotechnol Adv. 2016 Sep-Oct;34(5):532-549. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.12.014. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Biotechnol Adv. 2016. PMID: 26740171 Review.
-
Potential of the Flavonoid Quercetin to Prevent and Treat Cancer - Current Status of Research.Klin Onkol. 2018 Spring;31(3):184-190. doi: 10.14735/amko2018184. Klin Onkol. 2018. PMID: 30441971 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Towards an Integral Therapeutic Protocol for Breast Cancer Based upon the New H+-Centered Anticancer Paradigm of the Late Post-Warburg Era.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 10;21(20):7475. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207475. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential anti-cancer effects of quercetin on blood, prostate and lung cancers: An update.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 28;14:1077531. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1077531. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36926328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the effect of rhamnetin on mice injected with solid and ehrlich ascites tumor.Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 22;40(4):124. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01981-3. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36947317
-
The Antioxidant and Proapoptotic Effects of Sternbergia clusiana Bulb Ethanolic Extract on Triple-Negative and Estrogen-Dependent Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 24;12(3):529. doi: 10.3390/plants12030529. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771614 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of glioblastoma cell proliferation, invasion, and mechanism of action of a novel hydroxamic acid hybrid molecule.Cell Death Discov. 2018 Sep 26;4:41. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0103-0. eCollection 2018. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 30302275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mertens-Talcott S. U. & Percival S. S. Ellagic acid and quercetin interact synergistically with resveratrol in the induction of apoptosis and cause transient cell cycle arrest in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett 218, 141–151 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Mertens-Talcott S. U., Talcott S. T. & Percival S. S. Low concentrations of quercetin and ellagic acid synergistically influence proliferation, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in MOLT-4 human leukemia cells. J Nutr 133, 2669–2674 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Haghiac M. & Walle T. Quercetin induces necrosis and apoptosis in SCC-9 oral cancer cells. Nutr Cancer 53, 220–231 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Senthilkumar K. et al.. Quercetin regulates insulin like growth factor signaling and induces intrinsic and extrinsic pathway mediated apoptosis in androgen independent prostate cancer cells (PC-3). Mol Cell Biochem 344, 173–184 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Zhang H. et al.. Antitumor activities of quercetin and quercetin-5′,8-disulfonate in human colon and breast cancer cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol 50, 1589–1599 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

