Efficient Generation and Selection of Virtual Populations in Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Models
- PMID: 27069777
- PMCID: PMC4809626
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12063
Efficient Generation and Selection of Virtual Populations in Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Models
Abstract
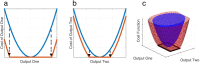
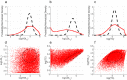
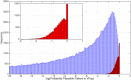
Quantitative systems pharmacology models mechanistically describe a biological system and the effect of drug treatment on system behavior. Because these models rarely are identifiable from the available data, the uncertainty in physiological parameters may be sampled to create alternative parameterizations of the model, sometimes termed "virtual patients." In order to reproduce the statistics of a clinical population, virtual patients are often weighted to form a virtual population that reflects the baseline characteristics of the clinical cohort. Here we introduce a novel technique to efficiently generate virtual patients and, from this ensemble, demonstrate how to select a virtual population that matches the observed data without the need for weighting. This approach improves confidence in model predictions by mitigating the risk that spurious virtual patients become overrepresented in virtual populations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improving the generation and selection of virtual populations in quantitative systems pharmacology models.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2018 Nov;139:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29902482
-
Alternate virtual populations elucidate the type I interferon signature predictive of the response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Jul 10;14:221. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-221. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23841912 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Populations for Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Models.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2486:129-179. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2265-0_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35437722
-
Linear-In-Flux-Expressions Methodology: Toward a Robust Mathematical Framework for Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Simulators.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2017 Jul 26;11:1177625017711414. doi: 10.1177/1177625017711414. eCollection 2017. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2017. PMID: 29581702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virtual reality simulation training for health professions trainees in gastrointestinal endoscopy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jun 13;(6):CD008237. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008237.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 17;8:CD008237. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008237.pub3 PMID: 22696375 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical responses to ERK inhibition in BRAFV600E-mutant colorectal cancer predicted using a computational model.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2017 Jun 2;3:14. doi: 10.1038/s41540-017-0016-1. eCollection 2017. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28649441 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 virtual patient cohort reveals immune mechanisms driving disease outcomes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jan 6:2021.01.05.425420. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.05.425420. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jul 14;17(7):e1009753. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009753 PMID: 33442689 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Virtual patient analysis identifies strategies to improve the performance of predictive biomarkers for PD-1 blockade.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 5;121(45):e2410911121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410911121. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39467131
-
An industry perspective on current QSP trends in drug development.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2024 Oct;51(5):511-520. doi: 10.1007/s10928-024-09905-y. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2024. PMID: 38443663 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale, mechanistic model of Rheumatoid Arthritis to enable decision making in late stage drug development.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024 Nov 4;10(1):126. doi: 10.1038/s41540-024-00454-1. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024. PMID: 39496637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der graaf, P.H. & Benson, N. Systems pharmacology: bridging systems biology and pharmacokinetics‐pharmacodynamics (PKPD) in drug discovery and development. Pharm. Res. 28, 1460–1464 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Allerheiligen, S.R.B. Next‐generation model‐based drug discovery and development: quantitative and systems pharmacology. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 88, 135–137 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Sorger, P.K. et al Quantitative and systems pharmacology in the post‐genomic era: new approaches to discovering drugs and understanding therapeutic mechanisms. A NIH White Paper by the QSP Workshop Group‐October 2011 (2011).
-
- Peterson, M.C. & Riggs, M.M. A physiologically based mathematical model of integrated calcium homeostasis and bone remodeling. Bone 46, 49–63 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Hallow, K.M. et al A model‐based approach to investigating the pathophysiological mechanisms of hypertension and response to antihypertensive therapies: extending the Guyton model. AJP Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 306, R647–R662 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

