Bioinformatic analysis of microRNA networks following the activation of the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) in mouse liver
- PMID: 27080131
- PMCID: PMC4975621
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.04.002
Bioinformatic analysis of microRNA networks following the activation of the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) in mouse liver
Abstract
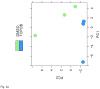
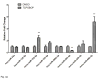
The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR; NR1I3) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily that functions as a xenosensor, serving to regulate xenobiotic detoxification, lipid homeostasis and energy metabolism. CAR activation is also a key contributor to the development of chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. The underlying pathways affected by CAR in these processes are complex and not fully elucidated. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as critical modulators of gene expression and appear to impact many cellular pathways, including those involved in chemical detoxification and liver tumor development. In this study, we used deep sequencing approaches with an Illumina HiSeq platform to differentially profile microRNA expression patterns in livers from wild type C57BL/6J mice following CAR activation with the mouse CAR-specific ligand activator, 1,4-bis-[2-(3,5,-dichloropyridyloxy)] benzene (TCPOBOP). Bioinformatic analyses and pathway evaluations were performed leading to the identification of 51 miRNAs whose expression levels were significantly altered by TCPOBOP treatment, including mmu-miR-802-5p and miR-485-3p. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of the differentially expressed microRNAs revealed altered effector pathways, including those involved in liver cell growth and proliferation. A functional network among CAR _targeted genes and the affected microRNAs was constructed to illustrate how CAR modulation of microRNA expression may potentially mediate its biological role in mouse hepatocyte proliferation. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Xenobiotic nuclear receptors: New Tricks for An Old Dog, edited by Dr. Wen Xie.
Keywords: Constitutive androstane receptor; Liver cancer; Mouse; TCPOBOP; microRNA.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
RNA-Seq reveals common and unique PXR- and CAR-_target gene signatures in the mouse liver transcriptome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1859(9):1198-1217. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27113289 Free PMC article.
-
Xenobiotic-induced hepatocyte proliferation associated with constitutive active/androstane receptor (CAR) or peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) is enhanced by pregnane X receptor (PXR) activation in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e61802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061802. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23626729 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide comparison of the inducible transcriptomes of nuclear receptors CAR, PXR and PPARα in primary human hepatocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1859(9):1218-1227. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.03.007. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26994748
-
PXR- and CAR-mediated herbal effect on human diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1859(9):1121-1129. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26906544 Review.
-
Nuclear receptors and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1859(9):1083-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26962021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse MicroRNAs-mRNA networks regulate the priming phase of mouse liver regeneration and of direct hyperplasia.Cell Prolif. 2022 Apr;55(4):e13199. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13199. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 35174557 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Xenobiotic Receptors: Beyond Chemical Disposition.Drug Metab Dispos. 2018 Sep;46(9):1361-1371. doi: 10.1124/dmd.118.081042. Epub 2018 May 14. Drug Metab Dispos. 2018. PMID: 29759961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo genome-wide binding interactions of mouse and human constitutive androstane receptors reveal novel gene _targets.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 19;46(16):8385-8403. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky692. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30102401 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of blood cells and plasma identifies tissue-specific miRNAs as potential novel circulating biomarkers in cattle.BMC Genomics. 2018 Apr 10;19(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4646-5. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29636028 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA crosstalk with nuclear receptors in liver disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 May 1;1867(5):166083. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166083. Epub 2021 Jan 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33497819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bae Y, Kemper JK, Kemper B. Repression of CAR-mediated transactivation of CYP2B genes by the orphan nuclear receptor, short heterodimer partner (SHP) 1. DNA Cell Biol. 2004;23:81. - PubMed
-
- Bai JX, Yan B, Zhao ZN, Xiao X, Qin WW, Zhang R, Jia LT, Meng YL, Jin BQ, Fan DM, Wang T, Yang AG. Tamoxifen represses miR-200 microRNAs and promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by up-regulating c-Myc in endometrial carcinoma cell lines. Endocrinology. 2013;154:635. - PubMed
-
- Benet M, Lahoz A, Guzman C, Castell JV, Jover R. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha) synergistically cooperate with constitutive androstane receptor to transactivate the human cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6) gene: application to the development of a metabolically competent human hepatic cell model. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:28457. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanco-Bose WE, Murphy MJ, Ehninger A, Offner S, Dubey C, Huang W, Moore DD, Trumpp A. C-Myc and its _target FoxM1 are critical downstream effectors of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) mediated direct liver hyperplasia. Hepatology. 2008;48:1302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

