Inhibition of D4 Dopamine Receptors on Insulin Receptor Expression and Effect in Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
- PMID: 27107134
- PMCID: PMC4843542
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002448
Inhibition of D4 Dopamine Receptors on Insulin Receptor Expression and Effect in Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
Abstract
Background: Ion transport in the renal proximal tubule (RPT), which is increased in essential hypertension, is regulated by numerous hormones and humoral factors, including insulin and dopamine. Activation of dopamine receptor inhibits sodium reabsorption, whereas activation of insulin receptor increases sodium reabsorption in RPTs, and hyperinsulinemic animals and patients have defective renal dopaminergic system. We presume that there is an inhibition of D4 receptor on insulin receptor expression and effect, and the regulation is lost in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs).
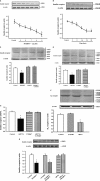
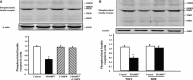
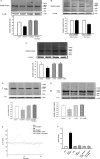
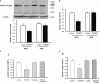
Methods and results: Insulin receptor expression was determined by immunoblotting, and Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity was detected in both Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) and SHR RPT cells. Stimulation of D4 receptor with PD168077 decreased expression of insulin receptors, which was blocked in the presence of the calcium-channel blocker, nicardipine (10(-6) mol/L per 24 hours), in cell culture medium without calcium or in the presence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor blocker (2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate [2-ADB]; 10(-6) mol/L per 24 hours), indicating that extracellular calcium entry and calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum were involved in the signal pathway. Stimulation of the insulin receptor stimulated Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity, whereas pretreatment with PD168077 for 24 hours decreased the inhibitory effects of insulin receptor on Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity in WKY cells. However, in SHR cells, inhibition of D4 receptor on insulin receptor expression and effect were lost.
Conclusions: Activation of D4 receptor inhibits insulin receptor expression in RPT cells from WKY rats. The aberrant inhibition of D4 receptor on insulin receptor expression and effect might be involved in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension.
Keywords: dopamine receptor; hypertension; insulin; renal proximal tubule cells.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of D4 dopamine receptor decreases angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in rat renal proximal tubule cells.Hypertension. 2015 Jan;65(1):153-60. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04038. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25368031 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of D3 dopamine receptor on dopamine D4 receptor expression and function in renal proximal tubule cells from Wistar-Kyoto rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 2016 Aug;34(8):1599-606. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000986. J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27254310
-
Activation of angiotensin II type 1 receptors increases D4 dopamine receptor expression in rat renal proximal tubule cells.Hypertens Res. 2017 Jul;40(7):652-657. doi: 10.1038/hr.2017.13. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Hypertens Res. 2017. PMID: 28230199
-
Dopamine-1 receptor G-protein coupling and the involvement of phospholipase A2 in dopamine-1 receptor mediated cellular signaling mechanisms in the proximal tubules of SHR.Clin Exp Hypertens. 1997 Jan-Feb;19(1-2):131-40. doi: 10.3109/10641969709080810. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1997. PMID: 9028641 Review.
-
Renal dopamine receptor signaling mechanisms in spontaneously hypertensive and Fischer 344 old rats.Clin Exp Hypertens. 1999 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):25-36. doi: 10.3109/10641969909068646. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10052639 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of D4 Dopamine Receptor on Na+-K+-ATPase Activity in Renal Proximal Tubule Cells.Cardiol Discov. 2023 Mar;3(1):24-29. doi: 10.1097/CD9.0000000000000076. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Cardiol Discov. 2023. PMID: 36969984 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Hypertension in Metabolic Syndrome: The Role of Fructose and Salt.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;24(5):4294. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054294. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DRD4 Mitigates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Association With PI3K/AKT Mediated Glucose Metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 27;11:619426. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.619426. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33584304 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Renal Dopaminergic System and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension.Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 1;9(2):139. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020139. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33535566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Rafts and Dopamine Receptor Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 24;21(23):8909. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238909. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosendorff C. Hypertension and coronary artery disease: a summary of the American Heart Association scientific statement. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007;9:790–795. - PubMed
-
- McDonough AA, Biemesderfer D. Does membrane trafficking play a role in regulating the sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3 in the proximal tubule? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003;12:533–541. - PubMed
-
- Hussain T, Lokhandwala MF. Renal dopamine receptors and hypertension. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2003;228:134–142. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286:H1597–H1602. - PubMed
-
- Wei Y, Chen K, Whaley‐Connell AT, Stump CS, Ibdah JA, Sowers JR. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance: role of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;294:R673–R680. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

