The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance but not of β cell function in a Chinese population with different glucose tolerance status
- PMID: 27267043
- PMCID: PMC4895977
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-016-0270-z
The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance but not of β cell function in a Chinese population with different glucose tolerance status
Abstract
Background: Triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio was a surrogate marker of IR; however, the relationship of TG/HDL-C with IR might vary by ethnicity. This study aims to investigate whether lipid ratios-TG/HDL-C, cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (TC/HDL-C) ratio, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C/HDL-C)) could be potential clinical markers of insulin resistance (IR) and β cell function and further to explore the optimal cut-offs in a Chinese population with different levels of glucose tolerance.
Methods: Four hundred seventy-nine subjects without a history of diabetes underwent a 75 g 2 h Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT). New-onset diabetes (n = 101), pre-diabetes (n = 186), and normal glucose tolerance (n = 192) were screened. IR was defined by HOMA-IR > 2.69. Based on indices (HOMA-β, early-phase disposition index [DI30], (ΔIns30/ΔGlu30)/HOMA-IR and total-phase index [DI120]) that indicated different phases of insulin secretion, the subjects were divided into two groups, and the lower group was defined as having inadequate β cell compensation. Logistic regression models and accurate estimates of the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROC) were obtained.
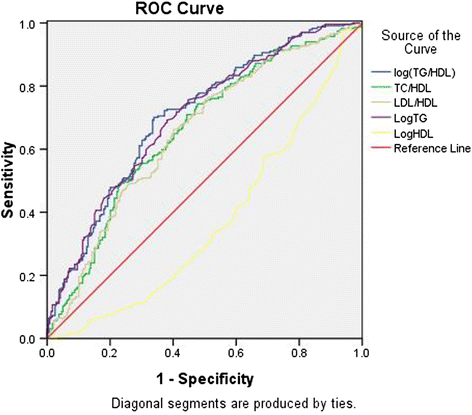
Results: In all of the subjects, TG/HDL, TC/HDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C, and TG were significantly associated with IR. The AUROCs of TG/HDL-C and TG were 0.71 (95 % CI: 0.66-0.75) and 0.71 (95 % CI: 0.65-0.75), respectively. The optimal cut-offs of TG/HDL-C and TG for IR diagnosis were 1.11 and 1.33 mmol/L, respectively. The AUROCs of TC/HDL-C and LDL-C/HDL-C were 0.66 and 0.65, respectively, but they were not acceptable for IR diagnosis. TG/HDL-C,LDL-C/HDL-C and TG were significantly associated with HOMA-β, but AUROCs were less than 0.50; therefore, the lipid ratios could not be predictors of basal β cell dysfunction. None of the lipid ratios was associated with early-phase insulin secretion. Only TG/HDL-C and TG were significantly correlated with total-phase insulin secretion, but they also were not acceptable predictors of total-phase insulin secretion (0.60 < AUROC < 0.70).
Conclusions: In a Chinese population with different levels of glucose tolerance, TG/HDL-C and TG could be the predictors of IR. The lipid ratios could not be reliable makers of β cell function in the population.
Keywords: Glucose tolerance status; Insulin resistance; Lipid ratios; β cell function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between lipid ratios and insulin resistance in a Chinese population.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 30;10(1):e0116110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116110. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25635876 Free PMC article.
-
Fasting plasma glucose is a stronger predictor of diabetes than triglyceride-glucose index, triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study.Acta Diabetol. 2018 Oct;55(10):1067-1074. doi: 10.1007/s00592-018-1195-y. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Acta Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 30066042
-
Relation of four nontraditional lipid profiles to diabetes in rural Chinese H-type hypertension population.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Oct 11;16(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0590-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 29020963 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of probiotic administration on patients with prediabetes: a meta-analysis and systematic review.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 2;20(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03695-y. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36324119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of lifestyle interventions on cardiovascular risk factors among adults without impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2017 May 11;12(5):e0176436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176436. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28493887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced glycation end products and diabetes and other metabolic indicators.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022 Jul 25;14(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00873-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35879776 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency and risk factors for recurrent gestational diabetes mellitus in primiparous women: a case control study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Feb 15;19(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0349-4. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 30767767 Free PMC article.
-
HDL Triglycerides: A New Marker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Risk.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 27;20(13):3151. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133151. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31252694 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory and Hyperinsulinemic Dietary Patterns Are Associated With Specific Profiles of Biomarkers Predictive of Chronic Inflammation, Glucose-Insulin Dysregulation, and Dyslipidemia in Postmenopausal Women.Front Nutr. 2021 Sep 20;8:690428. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.690428. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34616762 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive performance of lipid parameters in identifying undiagnosed diabetes and prediabetes: a cross-sectional study in eastern China.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Mar 24;22(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00984-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35331213 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous