B7-H4 expression indicates poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27383830
- PMCID: PMC11029220
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-016-1867-9
B7-H4 expression indicates poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
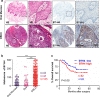
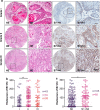
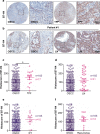
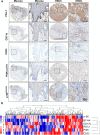
Checkpoint blockade therapy utilizing monoclonal antibodies to reactivate T cells and recover their antitumor activity makes an epoch in cancer immunotherapy. The role of B7-H4, a novel negative immune checkpoint, in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has still not been elucidated. In this study, tissue samples from human OSCC, which contains 165 primary OSCC, 48 oral epithelial dysplasia and 43 normal oral mucosa specimens, and Tgfbr1/Pten 2cKO mice OSCC model were stained with B7-H4 antibody to analyze the correlations between B7-H4 expression and clinicopathological characteristics. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to compare the survival of patients with high B7-H4 expression and patients with low B7-H4 expression. We found B7-H4 is highly expressed in human OSCC tissue, and the B7-H4 expression level was associated with the clinicopathological parameters containing pathological grade and lymph node status. Moreover, we confirmed that B7-H4 was overexpressed in Tgfbr1/Pten 2cKO mice OSCC model. Our data also indicated that patients with high B7-H4 expression had poor overall survival compared with those with low B7-H4 expression. Furthermore, this study demonstrated that B7-H4 was positively associated with PD-L1, CD11b, CD33, PI3Kα p110, and p-S6 (S235/236). Taken together, these findings suggest B7-H4 is a potential _target in the treatment of OSCC.
Keywords: B7-H4; Immune checkpoint; Immunotherapy; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Tissue microarray; Transgenic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Expression of LAMTOR5 Predicts Poor Prognosis and Is Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jun 2;16(6):783-792. doi: 10.7150/ijms.33415. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337951 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with an inflammatory phenotype.Pathology. 2016 Oct;48(6):574-80. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Pathology. 2016. PMID: 27590194
-
Overexpression of FAM3C is associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Apr;215(4):772-778. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.01.019. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30683473
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of p27 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2013 Dec 17;28(4):e329-35. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000035. Int J Biol Markers. 2013. PMID: 23787492 Review.
-
The role of B7-H4 in ovarian cancer immunotherapy: current status, challenges, and perspectives.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1426050. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1426050. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39267740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
OLR1 Is a Pan-Cancer Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Predictor Associated with EMT and Cuproptosis in HNSCC.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 17;24(16):12904. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612904. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629087 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint: The novel _target for antitumor therapy.Genes Dis. 2019 Dec 20;8(1):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.12.004. eCollection 2021 Jan. Genes Dis. 2019. PMID: 33569511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell differentiation trajectory predicts patient potential immunotherapy response and prognosis in gastric cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Feb 17;13(4):5928-5945. doi: 10.18632/aging.202515. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33612483 Free PMC article.
-
Single cell RNA sequencing reveals differentiation related genes with drawing implications in predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in gliomas.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 3;12(1):1872. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05686-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35115572 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression Patterns and Associated Clinical Parameters of Human Endogenous Retrovirus-H Long Terminal Repeat-Associating Protein 2 and Transmembrane and Immunoglobulin Domain Containing 2 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2019 Apr 7;2019:5421985. doi: 10.1155/2019/5421985. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31089395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stransky N, Egloff AM, Tward AD, Kostic AD, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Kryukov GV, Lawrence MS, Sougnez C, McKenna A, Shefler E, Ramos AH, Stojanov P, Carter SL, Voet D, Cortes ML, Auclair D, Berger MF, Saksena G, Guiducci C, Onofrio RC, Parkin M, Romkes M, Weissfeld JL, Seethala RR, Wang L, Rangel-Escareno C, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Melendez-Zajgla J, Winckler W, Ardlie K, Gabriel SB, Meyerson M, Lander ES, Getz G, Golub TR, Garraway LA, Grandis JR. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science. 2011;333(6046):1157–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1208130. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

