_targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 27516169
- PMCID: PMC5751421
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2016.151
_targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
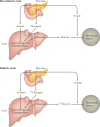
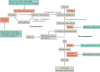
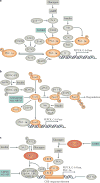
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by the dysregulation of glucose homeostasis, resulting in hyperglycaemia. Although current diabetes treatments have exhibited some success in lowering blood glucose levels, their effect is not always sustained and their use may be associated with undesirable side effects, such as hypoglycaemia. Novel antidiabetic drugs, which may be used in combination with existing therapies, are therefore needed. The potential of specifically _targeting the liver to normalize blood glucose levels has not been fully exploited. Here, we review the molecular mechanisms controlling hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogen storage, and assess the prospect of therapeutically _targeting associated pathways to treat type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of hepatic glucose production as a therapeutic _target in the treatment of diabetes.Curr Drug _targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2005 Mar;5(1):51-9. doi: 10.2174/1568008053174769. Curr Drug _targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2005. PMID: 15777204 Review.
-
Whole grains-derived functional ingredients against hyperglycemia: _targeting hepatic glucose metabolism.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(20):7268-7289. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2183382. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36847153 Review.
-
Metabolic Effects of Metformin in Humans.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(4):328-339. doi: 10.2174/1573399814666181009125348. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30306875 Review.
-
Intervention of hepatic glucose production. Small molecule regulators of potential _targets for Type 2 diabetes therapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004 Oct;4(8):897-908. doi: 10.2174/1389557043403459. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15544551 Review.
-
_targeting the CNS to treat type 2 diabetes.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 May;8(5):386-98. doi: 10.1038/nrd2874. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 19404312 Review.
Cited by
-
PHD3 regulates glucose metabolism by suppressing stress-induced signalling and optimising gluconeogenesis and insulin signalling in hepatocytes.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 24;8(1):14290. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32575-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30250231 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of systemic inflammation to permanence of KATP-induced neonatal diabetes in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Dec 1;315(6):E1121-E1132. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00137.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30226997 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Acute Phase Proteins in Stress and Inflammation-Induced T2D.Cells. 2022 Jul 11;11(14):2163. doi: 10.3390/cells11142163. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methanol-Extract/Fractions of Dacryodes edulis Leaves Ameliorate Hyperglycemia and Associated Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2019 Jan-Dec;24:2515690X19843832. doi: 10.1177/2515690X19843832. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31055945 Free PMC article.
-
1H-NMR-based metabolomics reveals the preventive effect of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharides on diabetes in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Mar 5;12(6):4049-4062. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4061. eCollection 2024 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38873458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, ga: US Department of health and human services; 2014. National diabetes statistics report: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States, 2014.
-
- Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world--a growing challenge. The New England journal of medicine. 2007;356:213–215. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes care. 1992;15:318–368. - PubMed
-
- Foretz M, Guigas B, Bertrand L, Pollak M, Viollet B. Metformin: from mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell metabolism. 2014;20:953–966. This work reviews the complexities surrounding the mechanism of action of metformin, the most widely used anti-diabetic drug. - PubMed
-
- Gribble FM, Reimann F. Sulphonylurea action revisited: the post-cloning era. Diabetologia. 2003;46:875–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

