Resistance of Transmitted Founder HIV-1 to IFITM-Mediated Restriction
- PMID: 27640936
- PMCID: PMC5075283
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.08.006
Resistance of Transmitted Founder HIV-1 to IFITM-Mediated Restriction
Abstract
Interferon-induced transmembrane proteins (IFITMs) restrict the entry of diverse enveloped viruses through incompletely understood mechanisms. While IFITMs are reported to inhibit HIV-1, their in vivo relevance is unclear. We show that IFITM sensitivity of HIV-1 strains is determined by the co-receptor usage of the viral envelope glycoproteins as well as IFITM subcellular localization within the _target cell. Importantly, we find that transmitted founder HIV-1, which establishes de novo infections, is uniquely resistant to the antiviral activity of IFITMs. However, viral sensitivity to IFITMs, particularly IFITM2 and IFITM3, increases over the first 6 months of infection, primarily as a result of neutralizing antibody escape mutations. Additionally, the ability to evade IFITM restriction contributes to the different interferon sensitivities of transmitted founder and chronic viruses. Together, these data indicate that IFITMs constitute an important barrier to HIV-1 transmission and that escape from adaptive immune responses exposes the virus to antiviral restriction.
Keywords: CD4; HIV-1; IFITM; antiviral restriction; co-receptor; escape; neutralization; transmitted founder virus; type 1 interferon.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
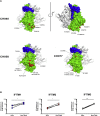
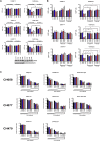
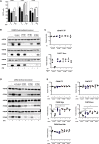
Comment in
-
Virus Infection: HIV-1 weighs up risks and benefits.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Nov;14(11):663. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.148. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27665720 No abstract available.
-
IFITMs: Important Factors In Trans-Mission of HIV-1.Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Oct 12;20(4):407-408. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.09.009. Cell Host Microbe. 2016. PMID: 27736636
Similar articles
-
Functional Heterogeneity of Mammalian IFITM Proteins against HIV-1.J Virol. 2021 Aug 25;95(18):e0043921. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00439-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34160255 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibition of HIV-1 Entry Imposed by Interferon Inducible Transmembrane Proteins Is Independent of Co-Receptor Usage.Viruses. 2018 Aug 7;10(8):413. doi: 10.3390/v10080413. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30087232 Free PMC article.
-
The V3 Loop of HIV-1 Env Determines Viral Susceptibility to IFITM3 Impairment of Viral Infectivity.J Virol. 2017 Mar 13;91(7):e02441-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02441-16. Print 2017 Apr 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28100616 Free PMC article.
-
IFITM proteins: Understanding their diverse roles in viral infection, cancer, and immunity.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jan;299(1):102741. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102741. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36435199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Viral Envelope Proteins in Determining Susceptibility of Viruses to IFITM Proteins.Viruses. 2024 Feb 5;16(2):254. doi: 10.3390/v16020254. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400030 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conference Report: LPMHealthcare Emerging Viruses 2023 (EVOX23): Pandemics-Learning from the Past and Present to Prepare for the Future.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 10;13(8):679. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080679. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204279 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of IFITM-IFITM Interactions by a Flow Cytometry-Based FRET Assay.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 8;20(16):3859. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163859. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31398796 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins Mediate Viral Evasion in Acute and Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Hepatology. 2019 Nov;70(5):1506-1520. doi: 10.1002/hep.30699. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 31062385 Free PMC article.
-
The Antiviral Activity of the Cellular Glycoprotein LGALS3BP/90K Is Species Specific.J Virol. 2018 Jun 29;92(14):e00226-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00226-18. Print 2018 Jul 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29743357 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting the Ins and Outs of HIV Replication: Cell-Intrinsic Antiretroviral Restrictions at the Plasma Membrane.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 4;8:1853. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01853. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29354117 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aasa-Chapman M.M., Hayman A., Newton P., Cornforth D., Williams I., Borrow P., Balfe P., McKnight A. Development of the antibody response in acute HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 2004;18:371–381. - PubMed
-
- Aasa-Chapman M.M., Holuigue S., Aubin K., Wong M., Jones N.A., Cornforth D., Pellegrino P., Newton P., Williams I., Borrow P., McKnight A. Detection of antibody-dependent complement-mediated inactivation of both autologous and heterologous virus in primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 2005;79:2823–2830. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

