Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 27660695
- PMCID: PMC5027002
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i17.354
Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
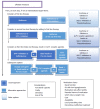
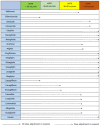
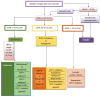
To achieve good metabolic control in diabetes and keep long term, a combination of changes in lifestyle and pharmacological treatment is necessary. Achieving near-normal glycated hemoglobin significantly, decreases risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications. At present there are different treatments, both oral and injectable, available for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Treatment algorithms designed to reduce the development or progression of the complications of diabetes emphasizes the need for good glycaemic control. The aim of this review is to perform an update on the benefits and limitations of different drugs, both current and future, for the treatment of T2DM. Initial intervention should focus on lifestyle changes. Moreover, changes in lifestyle have proven to be beneficial, but for many patients is a complication keep long term. Physicians should be familiar with the different types of existing drugs for the treatment of diabetes and select the most effective, safe and better tolerated by patients. Metformin remains the first choice of treatment for most patients. Other alternative or second-line treatment options should be individualized depending on the characteristics of each patient. This article reviews the treatments available for patients with T2DM, with an emphasis on agents introduced within the last decade.
Keywords: Future treatments; Injectable antidiabetic agents; Older people; Oral antidiabetic agents; Renal impairment; Treatment; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2005;65(3):385-411. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565030-00005. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15669880 Review.
-
Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422060-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. PMID: 15099124 Review.
-
Effects of antidiabetic drugs on the incidence of macrovascular complications and mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a new perspective on sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors.Ann Med. 2017 Feb;49(1):51-62. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2016.1226514. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Ann Med. 2017. PMID: 27535028 Review.
-
Short-term intensive insulin therapy could be the preferred option for new onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with HbA1c > 9.J Diabetes. 2017 Oct;9(10):890-893. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12581. Epub 2017 Aug 22. J Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28661564
-
[Treatment of diabetes in metabolic syndrome].Vnitr Lek. 2009 Jul-Aug;55(7-8):637-45. Vnitr Lek. 2009. PMID: 19731868 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Analyzing Amylin Aggregation Inhibition Through Quantum Dot Fluorescence Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11132. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011132. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456914 Free PMC article.
-
Anticipatory in silico vaccine designing based on specific antigenic epitopes from Streptococcus mutans against diabetic pathogenesis.In Silico Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 18;12(2):86. doi: 10.1007/s40203-024-00260-x. eCollection 2024. In Silico Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39310673
-
Effectiveness of the Beyond Good Intentions Program on Improving Dietary Quality Among People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Nutr. 2021 Mar 5;8:583125. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.583125. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33748169 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and proteomic signatures of type 2 diabetes subtypes in an Arab population.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 19;13(1):7121. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34754-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36402758 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Pancreas Development and Dysfunction Through the Lens of Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 29;9:629212. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.629212. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33996792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- International Diabetes Foundation. Diabetes: facts and figures [accessed 2016 Mar 22] Available from: http://www.idf.org/WDD15-guide/facts-and-figures.html.
-
- DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:318–368. - PubMed
-
- Ritz E, Rychlík I, Locatelli F, Halimi S. End-stage renal failure in type 2 diabetes: A medical catastrophe of worldwide dimensions. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;34:795–808. - PubMed
-
- del Cañizo-Gómez FJ, Moreira-Andrés MN. Cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Do we follow the guidelines? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;65:125–133. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

