REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants
- PMID: 27666373
- PMCID: PMC5065685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.08.016
REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants
Abstract
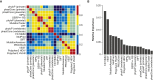
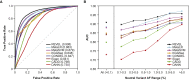
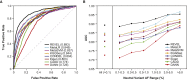
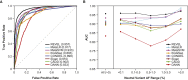
The vast majority of coding variants are rare, and assessment of the contribution of rare variants to complex traits is hampered by low statistical power and limited functional data. Improved methods for predicting the pathogenicity of rare coding variants are needed to facilitate the discovery of disease variants from exome sequencing studies. We developed REVEL (rare exome variant ensemble learner), an ensemble method for predicting the pathogenicity of missense variants on the basis of individual tools: MutPred, FATHMM, VEST, PolyPhen, SIFT, PROVEAN, MutationAssessor, MutationTaster, LRT, GERP, SiPhy, phyloP, and phastCons. REVEL was trained with recently discovered pathogenic and rare neutral missense variants, excluding those previously used to train its constituent tools. When applied to two independent test sets, REVEL had the best overall performance (p < 10-12) as compared to any individual tool and seven ensemble methods: MetaSVM, MetaLR, KGGSeq, Condel, CADD, DANN, and Eigen. Importantly, REVEL also had the best performance for distinguishing pathogenic from rare neutral variants with allele frequencies <0.5%. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for REVEL was 0.046-0.182 higher in an independent test set of 935 recent SwissVar disease variants and 123,935 putatively neutral exome sequencing variants and 0.027-0.143 higher in an independent test set of 1,953 pathogenic and 2,406 benign variants recently reported in ClinVar than the AUCs for other ensemble methods. We provide pre-computed REVEL scores for all possible human missense variants to facilitate the identification of pathogenic variants in the sea of rare variants discovered as sequencing studies expand in scale.
Copyright © 2016 American Society of Human Genetics. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison and integration of deleteriousness prediction methods for nonsynonymous SNVs in whole exome sequencing studies.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Apr 15;24(8):2125-37. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu733. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25552646 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of 13 in silico pathogenicity methods on cancer-related variants.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Jun;145:105434. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105434. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35364305
-
Comparison of Pathogenicity Prediction Tools on Somatic Variants.J Mol Diagn. 2020 Dec;22(12):1383-1392. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2020.08.007. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 33011441
-
Identifying Mendelian disease genes with the variant effect scoring tool.BMC Genomics. 2013;14 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S3-S3. Epub 2013 May 28. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23819870 Free PMC article.
-
The evaluation of tools used to predict the impact of missense variants is hindered by two types of circularity.Hum Mutat. 2015 May;36(5):513-23. doi: 10.1002/humu.22768. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Hum Mutat. 2015. PMID: 25684150 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of an autism-associated KCNMB2 variant, G124R, on BK channel properties.Curr Res Physiol. 2022 Sep 25;5:404-413. doi: 10.1016/j.crphys.2022.09.001. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36203817 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing performance of pathogenicity predictors using clinically relevant variant datasets.J Med Genet. 2021 Aug;58(8):547-555. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-107003. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 32843488 Free PMC article.
-
Germline Variants in DNA Damage Repair Genes and HOXB13 Among Black Patients With Early-Onset Prostate Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2022 Nov;6:e2200460. doi: 10.1200/PO.22.00460. JCO Precis Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36446039 Free PMC article.
-
Germline variant analysis from a cohort of patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia in Brazil.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2024 Jun 7;40:101100. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2024.101100. eCollection 2024 Sep. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2024. PMID: 38933898 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of CRB1 splicing in retinal organoids derived from a patient with adult-onset rod-cone dystrophy caused by the c.1892A>G and c.2548G>A variants.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Nov;8(11):e1489. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1489. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32931148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cirulli E.T., Goldstein D.B. Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through whole-genome sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:415–425. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

