Stress-Induced Locomotor Sensitization to Amphetamine in Adult, but not in Adolescent Rats, Is Associated with Increased Expression of ΔFosB in the Nucleus Accumbens
- PMID: 27672362
- PMCID: PMC5018519
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00173
Stress-Induced Locomotor Sensitization to Amphetamine in Adult, but not in Adolescent Rats, Is Associated with Increased Expression of ΔFosB in the Nucleus Accumbens
Abstract
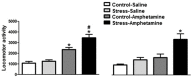
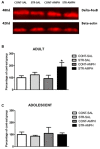
While clinical and pre-clinical evidence suggests that adolescence is a risk period for the development of addiction, the underlying neural mechanisms are largely unknown. Stress during adolescence has a huge influence on drug addiction. However, little is known about the mechanisms related to the interaction among stress, adolescence and addiction. Studies point to ΔFosB as a possible _target for this phenomenon. In the present study, adolescent and adult rats (postnatal day 28 and 60, respectively) were restrained for 2 h once a day for 7 days. Three days after their last exposure to stress, the animals were challenged with saline or amphetamine (1.0 mg/kg i.p.) and amphetamine-induced locomotion was recorded. Immediately after the behavioral tests, rats were decapitated and the nucleus accumbens was dissected to measure ΔFosB protein levels. We found that repeated restraint stress increased amphetamine-induced locomotion in both the adult and adolescent rats. Furthermore, in adult rats, stress-induced locomotor sensitization was associated with increased expression of ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens. Our data suggest that ΔFosB may be involved in some of the neuronal plasticity changes associated with stress induced-cross sensitization with amphetamine in adult rats.
Keywords: adolescence; amphetamine; behavioral sensitization; stress; ΔFosB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stress-induced cross-sensitization to amphetamine is related to changes in the dopaminergic system.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2012 Apr;119(4):415-24. doi: 10.1007/s00702-011-0720-8. Epub 2011 Oct 18. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2012. PMID: 22006016
-
Nucleus accumbens NMDA receptor activation regulates amphetamine cross-sensitization and deltaFosB expression following sexual experience in male rats.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Feb;101:154-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.023. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26391065
-
A single exposure to restraint stress induces behavioral and neurochemical sensitization to stimulating effects of amphetamine: involvement of NMDA receptors.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Jun;965:233-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04165.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12105099
-
DeltaFosB accumulation in ventro-medial caudate underlies the induction but not the expression of behavioral sensitization by both repeated amphetamine and stress.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Jan;27(1):191-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.06003.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18184321
-
Evidence of a complete independence of the neurobiological substrates for the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine.Neuroscience. 1995 Mar;65(2):385-95. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00524-9. Neuroscience. 1995. PMID: 7777156
Cited by
-
Interaction of stress and stimulants in female rats: Role of chronic stress on later reactivity to methamphetamine.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Dec 30;376:112176. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112176. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31449910 Free PMC article.
-
Long term effects of peripubertal stress on excitatory and inhibitory circuits in the prefrontal cortex of male and female mice.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Apr 1;14:100322. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100322. eCollection 2021 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 33869684 Free PMC article.
-
Mice Cohabiting With Familiar Conspecific in Chronic Stress Condition Exhibit Methamphetamine-Induced Locomotor Sensitization and Augmented Consolation Behavior.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Apr 18;16:835717. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.835717. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35517576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J., Nye H. E., Kelz M. B., Hiroi N., Nakabeppu Y., Hope B. T., et al. . (1995). Regulation of delta FosB and FosB-like proteins by electroconvulsive seizure and cocaine treatments. Mol. Pharmacol. 48, 880–889. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

