Towards Contactless Silent Speech Recognition Based on Detection of Active and Visible Articulators Using IR-UWB Radar
- PMID: 27801867
- PMCID: PMC5134471
- DOI: 10.3390/s16111812
Towards Contactless Silent Speech Recognition Based on Detection of Active and Visible Articulators Using IR-UWB Radar
Abstract
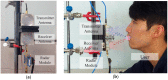
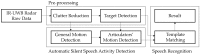
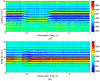
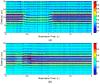
People with hearing or speaking disabilities are deprived of the benefits of conventional speech recognition technology because it is based on acoustic signals. Recent research has focused on silent speech recognition systems that are based on the motions of a speaker's vocal tract and articulators. Because most silent speech recognition systems use contact sensors that are very inconvenient to users or optical systems that are susceptible to environmental interference, a contactless and robust solution is hence required. Toward this objective, this paper presents a series of signal processing algorithms for a contactless silent speech recognition system using an impulse radio ultra-wide band (IR-UWB) radar. The IR-UWB radar is used to remotely and wirelessly detect motions of the lips and jaw. In order to extract the necessary features of lip and jaw motions from the received radar signals, we propose a feature extraction algorithm. The proposed algorithm noticeably improved speech recognition performance compared to the existing algorithm during our word recognition test with five speakers. We also propose a speech activity detection algorithm to automatically select speech segments from continuous input signals. Thus, speech recognition processing is performed only when speech segments are detected. Our testbed consists of commercial off-the-shelf radar products, and the proposed algorithms are readily applicable without designing specialized radar hardware for silent speech processing.
Keywords: IR-UWB radar; articulators’ detection; contactless silent speech recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
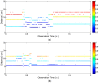
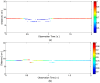
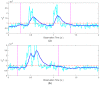
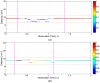
Similar articles
-
Short-Range Vital Signs Sensing Based on EEMD and CWT Using IR-UWB Radar.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Nov 30;16(12):2025. doi: 10.3390/s16122025. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27916877 Free PMC article.
-
Respiration Based Non-Invasive Approach for Emotion Recognition Using Impulse Radio Ultra Wide Band Radar and Machine Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 13;21(24):8336. doi: 10.3390/s21248336. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960430 Free PMC article.
-
Contactless Simultaneous Breathing and Heart Rate Detections in Physical Activity Using IR-UWB Radars.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 16;21(16):5503. doi: 10.3390/s21165503. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34450945 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Signal Processing Techniques for Remote Health Monitoring Using Impulse Radio UWB Transceiver.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Apr 27;20(9):2479. doi: 10.3390/s20092479. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32349382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Overview of Human Localization and Vital Sign Signal Measurement Using Handheld IR-UWB Through-Wall Radar.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 8;21(2):402. doi: 10.3390/s21020402. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33430061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silent speech command word recognition using stepped frequency continuous wave radar.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 9;12(1):4192. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07842-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35273225 Free PMC article.
-
Biosignal Sensors and Deep Learning-Based Speech Recognition: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 17;21(4):1399. doi: 10.3390/s21041399. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lane Detection Method with Impulse Radio Ultra-Wideband Radar and Metal Lane Reflectors.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jan 6;20(1):324. doi: 10.3390/s20010324. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31935964 Free PMC article.
-
Silent Speech Recognition as an Alternative Communication Device for Persons with Laryngectomy.IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process. 2017 Dec;25(12):2386-2398. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2740000. Epub 2017 Nov 28. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process. 2017. PMID: 29552581 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Silent Speech Interfaces Based on Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Radar.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;22(2):649. doi: 10.3390/s22020649. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juang B.-H., Rabiner L.R. Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics. 2nd ed. Elsevier; Boston, MA, USA: 2006. Speech Recognition, Automatic: History; pp. 806–819.
-
- Denby B., Schultz T., Honda K., Hueber T., Gilbert J.M., Brumberg J.S. Silent speech interfaces. Speech Commun. 2009;52:270–287. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2009.08.002. - DOI
-
- Schultz T., Wand M. Modeling coarticulation in EMG-based continuous speech recognition. Speech Commun. 2010;52:341–353. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2009.12.002. - DOI
-
- Wand M., Schulte C., Janke M., Schultz T. Array-based Electromyographic Silent Speech Interface; Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Bio-Inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS); Barcelona, Spain. 11–14 February 2013; pp. 89–96.
-
- Wand M., Himmelsbach A., Heistermann T., Janke M., Schultz T. Artifact Removal Algorithm for an EMG-Based Silent Speech Interface; Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; Osaka, Japan. 3–7 July 2013; pp. 5750–5753. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

