Angiopoietin-1 Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats
- PMID: 27873515
- PMCID: PMC5122639
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.206
Angiopoietin-1 Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Angiopoietin-1 Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats" by Huang ZW, et al. (Yonsei Med J 2017 Jan;58(1):206-216.).Yonsei Med J. 2022 Jun;63(6):601. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.6.601. Yonsei Med J. 2022. PMID: 35619585 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) is a critical factor for vascular stabilization and endothelial survival via inhibition of endothelial permeability and leukocyte- endothelium interactions. Hence, we hypothesized that treatment with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSCs) carrying the Ang1 gene (UCMSCs-Ang1) might be a potential approach for acute lung injury (ALI) induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Materials and methods: UCMSCs with or without transfection with the human Ang1 gene were delivered intravenously into rats one hour after intra-abdominal instillation of LPS to induce ALI. After the rats were sacrificed at 6 hours, 24 hours, 48 hours, 8 days, and 15 days post-injection of LPS, the serum, the lung tissues, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were harvested for analysis, respectively.
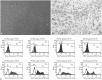
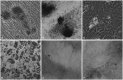
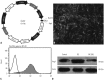
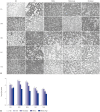
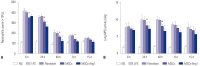
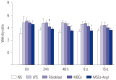
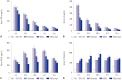
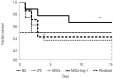
Results: Administration of fluorescence microscope confirmed the increased presence of UCMSCs in the injured lungs. The evaluation of UCMSCs and UCMSCs-Ang1 actions revealed that Ang1 overexpression further decreased the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, TGF-β₁, and IL-6 and increased the expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in the injured lungs. This synergy caused a substantial decrease in lung airspace inflammation and vascular leakage, characterized by significant reductions in wet/dry ratio, differential neutrophil counts, myeloperoxidase activity, and BALF. The rats treated by UCMSCs-Ang1 showed improved survival and lower ALI scores.
Conclusion: UCMSCs-Ang1 could improve both systemic inflammation and alveolar permeability in ALI. UC-derived MSCs-based Ang1 gene therapy may be developed as a potential novel strategy for the treatment of ALI.
Keywords: Angiopoietin-1; acute lung injury; human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-based angiopoietin-1 gene therapy for acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice.J Pathol. 2008 Mar;214(4):472-81. doi: 10.1002/path.2302. J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18213733
-
Comparative Effects of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment via Different Routes on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Jun 17;29(6):217. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2906217. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38940047
-
A study on the role of apoptotic human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in bleomycin-induced acute lung injury in rat models.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Mar;20(5):969-82. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27010158
-
The optimal transplantation strategy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury: a systematic review and network meta-analysis based on animal studies.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Sep 2;13(1):441. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03103-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36056386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy as a new therapeutic approach for acute inflammation.Life Sci. 2023 Jan 1;312:121206. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121206. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36403645 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Preclinical Models of Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024 Apr 15;13(4):346-361. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szae003. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38381583 Free PMC article.
-
What is the impact of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on clinical treatment?Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Dec 1;11(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02011-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33261658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Attenuate Infection-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Animal Experiments: A Meta-Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720969186. doi: 10.1177/0963689720969186. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33164559 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes: bioactive ways of tissue injury repair.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Mar 15;11(3):1230-1240. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30972158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells alleviate neuroinflammation by modulating M1/M2 polarization in cell and rat Parkinson's disease models.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 13;14(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03330-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37055866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gharib SA, Liles WC, Matute-Bello G, Glenny RW, Martin TR, Altemeier WA. Computational identification of key biological modules and transcription factors in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:653–658. - PubMed
-
- Slutsky AS, Hudson LD. PEEP or no PEEP--lung recruitment may be the solution. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1839–1841. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

