Ethical imperatives of timely access to orphan drugs: is possible to reconcile economic incentives and patients' health needs?
- PMID: 28057032
- PMCID: PMC5217554
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-016-0551-7
Ethical imperatives of timely access to orphan drugs: is possible to reconcile economic incentives and patients' health needs?
Abstract
Background: More than 6,800 rare diseases and conditions have been identified in the US, which affect 25-30 million Americans. In 1983, the US Congress enacted the Orphan Drug Act (ODA) to encourage the development and marketing of drugs to treat rare diseases and conditions. This study analyzed all orphan designations and FDA approvals since 1983 through 2015, discussed the effectiveness of incentives for the development of treatments for rare diseases, and reflected on the ethical imperatives for timely access to orphan drugs.
Methods: Study data were derived from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Orange Book and the Office of Orphan Drugs Development. A search was conducted to assess literature on the ethical principles and economic incentives for the development of orphan drugs.
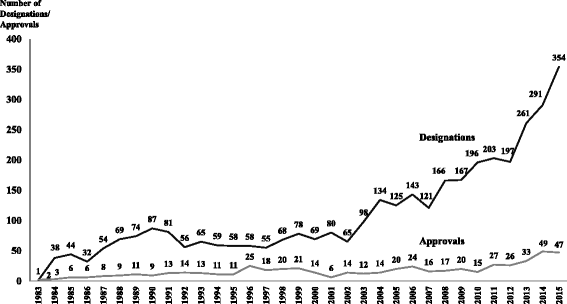
Results: In the period 1983-2015, the FDA granted 3,647 orphan drug designations and 554 orphan drug approvals. The orphan drug approvals corresponded to 438 different brand names. Cancer was the therapeutic area with the highest number of approvals. The increased number of patients with rare diseases and the growth in the cost of orphan drugs pose a significant economic burden for patients, public programs and private third party payers. Regulatory differences to qualify for orphan designation and various population thresholds employed by the FDA and the European Medicines Agency lead to further unmet health needs for patients with rare diseases and aggravate health inequities. There is no societal consensus on the population and economic thresholds, the drug effectiveness indicator(s), or the societal value to be placed for the approval and reimbursement of orphan drugs.
Conclusion: Orphan drug development and marketing in the US concentrate in few therapeutic areas. Despite the increase in the number of FDA approved orphan drugs, the unmet needs of patients with rare diseases evidence that the current incentives are not efficiently stimulating orphan drug development. There is need to balance economic incentives to stimulate the development and marketing of orphan drugs without jeopardizing patients' access to treatment. Thus, aligning pharmaceutical companies' incentives with societal budgetary constraints is necessary and the ethical imperatives of timely access to orphan drugs need to be agreed upon.
Keywords: Economic incentives; Ethical aspects; FDA; Orphan diseases; Orphan drugs; Rare diseases; Research and development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Special FDA designations for drug development: orphan, fast track, accelerated approval, priority review, and breakthrough therapy.Eur J Health Econ. 2024 Aug;25(6):979-997. doi: 10.1007/s10198-023-01639-x. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Eur J Health Econ. 2024. PMID: 37962724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incentives for orphan drug research and development in the United States.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2008 Dec 16;3:33. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-3-33. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2008. PMID: 19087348 Free PMC article.
-
The US Orphan Drug Act: rare disease research stimulator or commercial opportunity?Health Policy. 2010 May;95(2-3):216-28. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2009.12.001. Epub 2009 Dec 29. Health Policy. 2010. PMID: 20036435
-
Novel Treatments for Rare Cancers: The U.S. Orphan Drug Act Is Delivering-A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Oncologist. 2016 Apr;21(4):487-93. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0397. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27022038 Free PMC article.
-
Incentivizing Orphan Product Development: United States Food and Drug Administration Orphan Incentive Programs.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1031:183-196. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67144-4_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29214572 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the value of orphan drugs using conventional cost-effectiveness analysis: Is it fit for purpose?Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Apr 5;17(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02283-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 35382853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inclusion of Infants and Neonates in Pediatric Orphan Product Approvals.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Oct;110(4):997-1003. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2306. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34028811 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding on the Genetic Basis of Key Metabolic Disorders: A Review.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;11(9):1308. doi: 10.3390/biology11091308. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) in rare diseases: a landscape analysis from funders.Eur J Hum Genet. 2020 Feb;28(2):174-181. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0513-3. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31537898 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced therapy medicinal products: value judgement and ethical evaluation in health technology assessment.Eur J Health Econ. 2020 Apr;21(3):311-320. doi: 10.1007/s10198-019-01147-x. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Eur J Health Econ. 2020. PMID: 31919703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic Diseases: The Leading Causes of Death and Disability in the United States. 2016. http://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/overview/index.htm. Accessed 14 Aug 2016.
-
- National Institutes of Health. Genetic and Rare Disease Information Center. 2008. http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Accessed 18 Mar 2016.
-
- United States Congress: Rare diseases Act of 2002. Public Law 107–280.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical