Exosomal biomarkers of brain insulin resistance associated with regional atrophy in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 28105773
- PMCID: PMC5342917
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23494
Exosomal biomarkers of brain insulin resistance associated with regional atrophy in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Brain insulin resistance (IR), which depends on insulin-receptor-substrate-1 (IRS-1) phosphorylation, is characteristic of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously, we demonstrated higher pSer312-IRS-1 (ineffective insulin signaling) and lower p-panTyr-IRS-1 (effective insulin signaling) in neural origin-enriched plasma exosomes of AD patients vs.
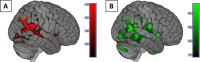
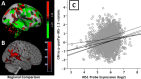
Controls: Here, we hypothesized that these exosomal biomarkers associate with brain atrophy in AD. We studied 24 subjects with biomarker-supported probable AD (low CSF Aβ42 ). Exosomes were isolated from plasma, enriched for neural origin using immunoprecipitation for L1CAM, and measured for pSer312 - and p-panTyr-IRS-1 phosphotypes. MPRAGE images were segmented by brain tissue type and voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis for gray matter against pSer312 - and p-panTyr-IRS-1 was conducted. Given the regionally variable brain expression of IRS-1, we used the Allen Brain Atlas to make spatial comparisons between VBM results and IRS-1 expression. Brain volume was positively associated with P-panTyr-IRS-1 and negatively associated with pSer312 -IRS-1 in a strikingly similar regional pattern (bilateral parietal-occipital junction, R middle temporal gyrus). This volumetric association pattern was spatially correlated with Allen Human Brain atlas normal brain IRS-1 expression. Exosomal biomarkers of brain IR are thus associated with atrophy in AD as could be expected by their pathophysiological roles and do so in a pattern that reflects regional IRS-1 expression. Furthermore, neural-origin plasma exosomes may recover molecular signals from specific brain regions. Hum Brain Mapp 38:1933-1940, 2017. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; IRS-1; biomarker; exosomes; insulin resistance; magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysfunctionally phosphorylated type 1 insulin receptor substrate in neural-derived blood exosomes of preclinical Alzheimer's disease.FASEB J. 2015 Feb;29(2):589-96. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-262048. Epub 2014 Oct 23. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25342129 Free PMC article.
-
The association between biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid and structural changes in the brain in patients with Alzheimer's disease.J Intern Med. 2014 Apr;275(4):418-27. doi: 10.1111/joim.12164. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24237038
-
Preclinical cerebrospinal fluid and volumetric magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers in Swedish familial Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43(4):1393-402. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140339. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25182737
-
Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer's disease.J Neurovirol. 2019 Oct;25(5):702-709. doi: 10.1007/s13365-018-0695-4. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Neurovirol. 2019. PMID: 30610738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on potential links between type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Aug;47(8):6347-6356. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05693-z. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32740795 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Extracellular Vesicle α-Synuclein Level in Patients with Parkinson's Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 May 17;11(5):744. doi: 10.3390/biom11050744. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34067663 Free PMC article.
-
Brain insulin resistance and altered brain glucose are related to memory impairments in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2019 Jun;208:324-330. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2019.01.031. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Schizophr Res. 2019. PMID: 30760413 Free PMC article.
-
The human neurosecretome: extracellular vesicles and particles (EVPs) of the brain for intercellular communication, therapy, and liquid-biopsy applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 17;10:1156821. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1156821. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37266331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does insulin resistance influence neurodegeneration in non-diabetic Alzheimer's subjects?Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Feb 17;13(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00784-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33597002 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects and challenges in using neuronal extracellular vesicles in biomarker research.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Sep;20(9):6632-6638. doi: 10.1002/alz.13918. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39009473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert, MS , DeKosky, ST , Dickson, D , Dubois, B , Feldman, HH , Fox, NC , Gamst, A , Holtzman, DM , Jagust, WJ , Petersen, RC , Snyder, PJ , Carrillo, MC , Thies, B , Phelps, CH (2011): The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging‐Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 7:270–279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000): Voxel‐based morphometry–The methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005): Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26:839–851. - PubMed
-
- Bomfim, TR , Forny‐Germano, L , Sathler, LB , Brito‐Moreira, J , Houzel, JC , Decker, H , Silverman, MA , Kazi, H , Melo, HM , McClean, PL , Holscher, C , Arnold, SE , Talbot, K , Klein, WL , Munoz, DP , Ferreira, ST , De Felice, FG (2012): An anti‐diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's disease‐associated Abeta oligomers. J Clin Invest 122:1339–1353. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

