Antifungal Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains Isolated from Natural Honey against Pathogenic Candida Species
- PMID: 28154488
- PMCID: PMC5287163
- DOI: 10.5941/MYCO.2016.44.4.302
Antifungal Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains Isolated from Natural Honey against Pathogenic Candida Species
Abstract
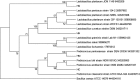
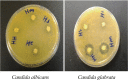
The role of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in honey as antifungal activity has received little attention and their mechanism of inhibitory of fungi is not fully understood. In this study, LAB were isolated from honey samples from Malaysia, Libya, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen. Twenty-five isolates were confirmed LAB by catalase test and Gram staining, and were screened for antifungal activity. Four LAB showed inhibitory activity against Candida spp. using the dual agar overlay method. And they were identified as Lactobacillus plantarum HS isolated from Al-Seder honey, Lactobacillus curvatus HH isolated from Al-Hanon honey, Pediococcus acidilactici HC isolated from Tualang honey and Pediococcus pentosaceus HM isolated from Al-Maray honey by the 16S rDNA sequence. The growth of Candida glabrata ATCC 2001 was strongly inhibited (>15.0 mm) and (10~15 mm) by the isolates of L. curvatus HH and P. pentosaceus HM, respectively. The antifungal activity of the crude supernatant (cell free supernatant, CFS) was evaluated using well diffusion method. The CFS showed high antifungal activity against Candida spp. especially The CFS of L. curvatus HH was significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited growth of C. glabrata ATCC 2001, C. parapsilosis ATCC 2201, and C. tropicalis ATCC 750 with inhibitory zone 22.0, 15.6, and 14.7 mm, respectively. While CFS of P. pentosaceus HM was significantly (p < 0.05) effective against C. krusei, C. glabrata, and C. albicans with inhibition zone 17.2, 16.0, and 13.3 mm, respectively. The results indicated that LAB isolated from honey produced compounds which can be used to inhibit the growth of the pathogenic Candida species.
Keywords: Antifungal activity; Honey; Lactic acid bacteria; Pathogenic Candida species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antifungal effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum against different oral Candida species isolated from HIV/ AIDS patients: an in vitro study.J Oral Microbiol. 2020 May 25;12(1):1769386. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2020.1769386. J Oral Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32922676 Free PMC article.
-
Fungicidal efficacy of various honeys against fluconazole-resistant Candida species isolated from HIV+ patients with candidiasis.J Mycol Med. 2017 Jun;27(2):159-165. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Mycol Med. 2017. PMID: 28159362
-
Cell-free culture supernatants of Lactobacillus spp. and Pediococcus spp. inhibit growth of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs in Thailand.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Jan 29;18(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03140-8. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35093088 Free PMC article.
-
Candida and candidaemia. Susceptibility and epidemiology.Dan Med J. 2013 Nov;60(11):B4698. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24192246 Review.
-
Non-albicans Candida spp. causing fungaemia: pathogenicity and antifungal resistance.J Hosp Infect. 2002 Apr;50(4):243-60. doi: 10.1053/jhin.2001.1151. J Hosp Infect. 2002. PMID: 12014897 Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotic Properties and Potentiality of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains for the Biological Control of Chalkbrood Disease.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 May 12;7(5):379. doi: 10.3390/jof7050379. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066127 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomic Analysis of Lactobacillus curvatus Reveals Two Lineages Distinguished by Genes for Fermenting Plant-Derived Carbohydrates.Genome Biol Evol. 2018 Jun 1;10(6):1516-1525. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy106. Genome Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29850855 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery mechanism can enhance probiotic activity against honey bee pathogens.ISME J. 2023 Sep;17(9):1382-1395. doi: 10.1038/s41396-023-01422-z. Epub 2023 Jun 14. ISME J. 2023. PMID: 37311937 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Properties, Functional Characterisation and Application of Fructobacillus fructosus and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Isolated from Artisanal Honey.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023 Oct;15(5):1406-1423. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09988-4. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023. PMID: 36173591 Free PMC article.
-
Biotechnological and Medical Aspects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Used for Plant Protection: A Comprehensive Review.BioTech (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;11(3):40. doi: 10.3390/biotech11030040. BioTech (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36134914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weston RJ, Brocklebank LK. The oligosaccharide composition of some New Zealand honeys. Food Chem. 1999;64:33–37.
-
- Molan P. The antibacterial properties of honey. Chem N Z. 1995;59:10–14.
-
- Endo A, Futagawa-Endo Y, Dicks LM. Isolation and characterization of fructophilic lactic acid bacteria from fructose-rich niches. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2009;32:593–600. - PubMed
-
- Adeniyi BA, Ayeni FA, Ogunbanwo ST. Antagonistic activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Nigerian fermented dairy food against organisms implicated in urinary tract infection. Biotechnology. 2006;5:183–188.
-
- Sezer Ç, Güven A. Investigation of bacteriocin production capability of lactic acid bacteria isolated from foods. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg. 2009;15:45–50.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
