Mechanism of the blood pressure-lowering effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in obese patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 28391776
- PMCID: PMC5385592
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-017-0125-x
Mechanism of the blood pressure-lowering effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in obese patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are reported to have BP-lowering effect in addition to blood glucose-lowering effect, however, its mechanism is still unknown. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism of blood pressure (BP) lowering effects of SGLT2 inhibitors using 24-h urinary collection in obese type 2 diabetes patients.
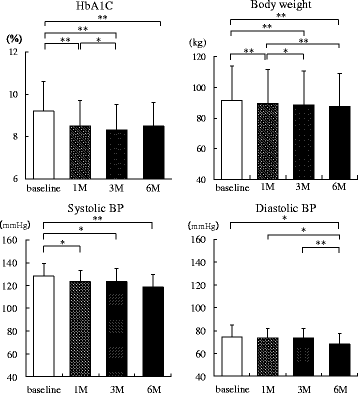
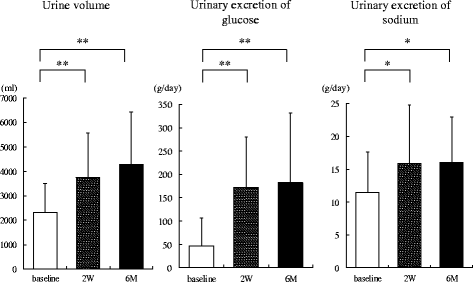
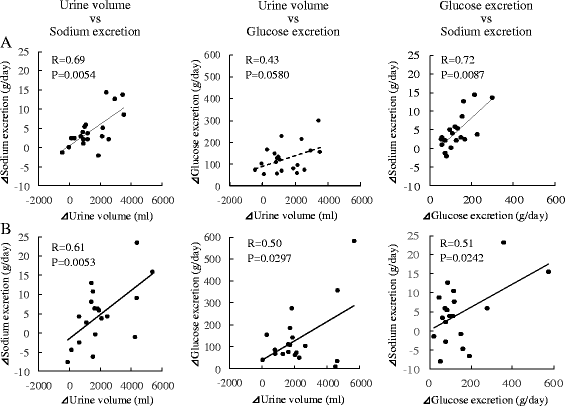
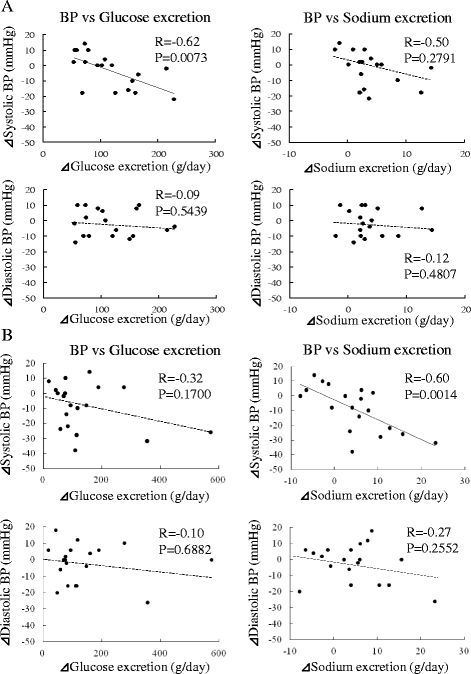
Methods: Twenty patients with type 2 diabetes (age 48.2 ± 10.7 years, BMI 33.0 ± 4.9 kg/m2) were enrolled. Urine volume, 24-h urinary glucose and sodium excretion, and BP at baseline and 2 weeks and 6 months after administration were measured. Body weight, glycosylated hemoglobin, and BP were evaluated before and 1, 3, and 6 months after SGLT2 inhibitor administration. We evaluated the changes in urine volume and urinary excretion of glucose and sodium as well as correlations among urine volume and urinary sodium glucose excretion at 2 weeks and 6 months after administration of the SGLT2 inhibitors. Furthermore, we investigated the correlations between changes in BP and urinary excretion of sodium and glucose at the same time.
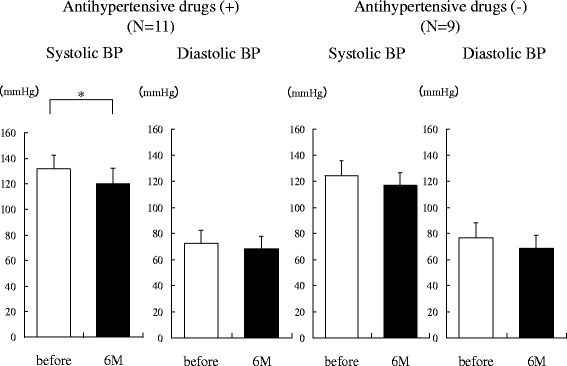
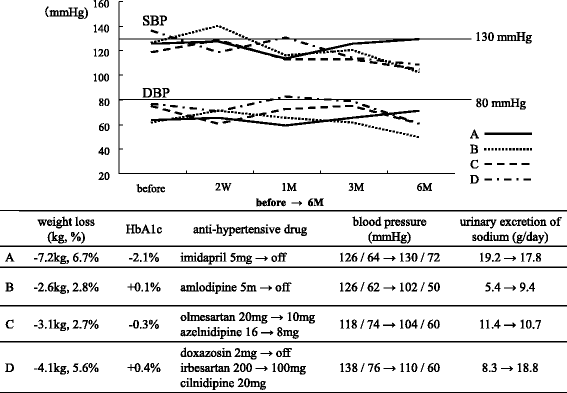
Results: Two weeks after administration, systolic BP (SBP) significantly decreased (128.5 ± 11.0 to 123.2 ± 9.8 mmHg, P = 0.0314), but diastolic BP (DBP) did not (74.4 ± 10.4 to 73.4 ± 8.5 mmHg, P = 0.5821). The decreased SBP significantly correlated with increased urinary glucose excretion (R = -0.62, P = 0.0073), but not increased urinary sodium excretion. At 6 months, SBP (118.6 ± 11.0 mmHg, P = 0.0041) and DBP (68.4 mmHg, P = 0.0363) significantly decreased. The decreased SBP significantly correlated with increased urinary sodium excretion (R = -0.60, P = 0.0014), but not increased urinary glucose excretion.
Conclusions: SGLT2 inhibitors significantly decreased SBP after 1 month and DBP after 6 months in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. The main mechanism of the BP-lowering effect may be plasma volume reduction by osmotic diuresis at 2 weeks and by natriuresis at 6 months after SGLT2 inhibitor administration.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Natriuresis; Osmotic diuresis; SGLT2 inhibitor; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2016 Oct 27;12:393-405. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S111991. eCollection 2016. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2016. PMID: 27822054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2015 Jan;75(1):33-59. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0337-y. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25488697 Review.
-
Switching from low-dose thiazide diuretics to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor improves various metabolic parameters without affecting blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension.J Diabetes Investig. 2018 Jul;9(4):875-881. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12774. Epub 2017 Dec 4. J Diabetes Investig. 2018. PMID: 29110406 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and their mechanism for improving glycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.Postgrad Med. 2014 Oct;126(6):33-48. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2014.10.2819. Postgrad Med. 2014. PMID: 25414933 Review.
-
Potential role of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of hypertension.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Mar;25(2):81-6. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000199. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26808705 Review.
Cited by
-
Fractal properties and morphological investigation of Nano hydrochlorothiazide is used to treat hypertension.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Nov 9;19(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0259-5. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30413182 Free PMC article.
-
Renal physiology of glucose handling and therapeutic implications.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020 Jan 1;35(Suppl 1):i3-i12. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfz230. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32003835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying some major common risk factors of stroke.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 18;8(8):e10218. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10218. eCollection 2022 Aug. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36060992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diuretic Effects of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Their Influence on the Renin-Angiotensin System.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 1;20(3):629. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030629. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30717173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pregnant alpha-1-microglobulin (A1M) knockout mice exhibit features of kidney and placental damage, hemodynamic changes and intrauterine growth restriction.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 26;10(1):20625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77561-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33244052 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

