Ceramide synthesis regulates T cell activity and GVHD development
- PMID: 28515365
- PMCID: PMC5436544
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.91701
Ceramide synthesis regulates T cell activity and GVHD development
Abstract
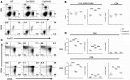
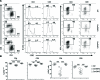
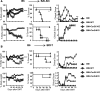
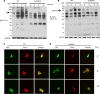
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) is an effective immunotherapy for a variety of hematologic malignances, yet its efficacy is impeded by the development of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). GVHD is characterized by activation, expansion, cytokine production, and migration of alloreactive donor T cells. Hence, strategies to limit GVHD are highly desirable. Ceramides are known to contribute to inflammation and autoimmunity. However, their involvement in T-cell responses to alloantigens is undefined. In the current study, we specifically characterized the role of ceramide synthase 6 (CerS6) after allo-HCT using genetic and pharmacologic approaches. We found that CerS6 was required for optimal T cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production in response to alloantigen and for subsequent induction of GVHD. However, CerS6 was partially dispensable for the T cell-mediated antileukemia effect. At the molecular level, CerS6 was required for efficient TCR signal transduction, including tyrosine phosphorylation, ZAP-70 activation, and PKCθ/TCR colocalization. Impaired generation of C16-ceramide was responsible for diminished allogeneic T cell responses. Furthermore, _targeting CerS6 using a specific inhibitor significantly reduced T cell activation in mouse and human T cells in vitro. Our study provides a rationale for _targeting CerS6 to control GVHD, which would enhance the efficacy of allo-HCT as an immunotherapy for hematologic malignancies in the clinic.
Keywords: Immunology; Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ceramide synthase 6 impacts T-cell allogeneic response and graft-versus-host disease through regulating N-RAS/ERK pathway.Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1907-1915. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01581-6. Epub 2022 May 5. Leukemia. 2022. PMID: 35513703 Free PMC article.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
Serine protease inhibitor 6 protects alloreactive T cells from Granzyme B-mediated mitochondrial damage without affecting graft-versus-tumor effect.Oncoimmunology. 2017 Nov 16;7(3):e1397247. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1397247. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 29399396 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Deacetylase SIRT3 Plays an Important Role in Donor T Cell Responses after Experimental Allogeneic Hematopoietic Transplantation.J Immunol. 2018 Dec 1;201(11):3443-3455. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800148. Epub 2018 Nov 2. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30389773 Free PMC article.
-
Antileukemia and antitumor effects of the graft-versus-host disease: a new immunovirological approach.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2010 Dec;57(4):253-347. doi: 10.1556/AMicr.57.2010.4.2. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2010. PMID: 21183421 Review.
Cited by
-
Ceramide Synthase 6 Deficiency Enhances Inflammation in the DSS model of Colitis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):1627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20102-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374263 Free PMC article.
-
Achievement of Tolerance Induction to Prevent Acute Graft-vs.-Host Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 6;10:309. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00309. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30906290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The druggable transcription factor Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease.J Clin Invest. 2022 Nov 1;132(21):e143950. doi: 10.1172/JCI143950. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 36074578 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling networks in immunometabolism.Cell Res. 2020 Apr;30(4):328-342. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0301-1. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32203134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids in embryonic development, cell cycle regulation, and stemness - Implications for polyploidy in tumors.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Jun;81:206-219. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.027. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33429049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

