Insights into the prevalence and underlying causes of clonal variation through transcriptomic analysis in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 28534062
- PMCID: PMC5486821
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-017-8317-2
Insights into the prevalence and underlying causes of clonal variation through transcriptomic analysis in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
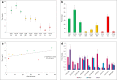
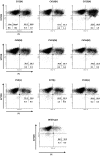
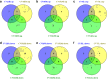
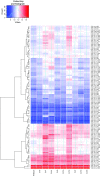
Clonal variation, wherein a range of specific productivities of secreted proteins are observed from supposedly identical transformants, is an accepted aspect of working with Pichia pastoris. It means that a significant number of transformants need to be tested to obtain a representative sample, and in commercial protein production, companies regularly screen thousands of transformants to select for the highest secretor. Here, we have undertaken a detailed investigation of this phenomenon by characterising clones transformed with the human serum albumin gene. The titers of nine clones, each containing a single copy of the human serum albumin gene (identified by qPCR), were measured and the clones grouped into three categories, namely, high-, mid- and low-level secretors. Transcriptomic analysis, using microarrays, showed that no regulatory patterns consistently correlated with titer, suggesting that the causes of clonal variation are varied. However, a number of physiological changes appeared to underlie the differences in titer, suggesting there is more than one biochemical signature for a high-secreting strain. An anomalous low-secreting strain displaying high transcript levels that appeared to be nutritionally starved further emphasises the complicated nature of clonal variation.
Keywords: Clonal variation; ER-associated degradation; Pichia pastoris/Komagataella phaffii; Protein expression; Transcriptomic analysis/microarray; Unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
Funding was provided to RA by Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) as a CASE studentship with Avecia Biologics Ltd. (now Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Plasmid Design and Type of Integration Event on Recombinant Protein Expression in Pichia pastoris.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Mar 1;84(6):e02712-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02712-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29330186 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and transcriptomics of Pichia pastoris.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 5;17:550. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2876-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27495311 Free PMC article.
-
A switchable secrete-and-capture system enables efficient selection of Pichia pastoris clones producing high yields of Fab fragments.J Immunol Methods. 2022 Dec;511:113383. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113383. Epub 2022 Nov 8. J Immunol Methods. 2022. PMID: 36356896
-
Quo vadis? The challenges of recombinant protein folding and secretion in Pichia pastoris.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Apr;99(7):2925-38. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6470-z. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25722021 Review.
-
Molecular strategies to increase the levels of heterologous transcripts in Komagataella phaffii for protein production.Bioengineered. 2017 Sep 3;8(5):441-445. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2017.1296613. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Bioengineered. 2017. PMID: 28399696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Cell Approach to Monitor the Unfolded Protein Response During Biotechnological Processes With Pichia pastoris.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 27;10:335. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00335. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30873140 Free PMC article.
-
Current achievements, strategies, obstacles, and overcoming the challenges of the protein engineering in Pichia pastoris expression system.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 8;40(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03851-6. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38062216 Review.
-
Design of a novel switchable antibody display system in Pichia pastoris.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;106(18):6209-6224. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12108-5. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35953606
-
Epigenetic engineering of yeast reveals dynamic molecular adaptation to methylation stress and genetic modulators of specific DNMT3 family members.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 May 7;48(8):4081-4099. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa161. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32187373 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of the unfolded protein response pathway in Pichia pastoris: enhancing production of secreted recombinant proteins.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jun;105(11):4397-4414. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11336-5. Epub 2021 May 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34037840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bardini M, Labra M, Winfield M, Sala F. Antibiotic-induced DNA methylation changes in calluses of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss Org. 2003;72:157–162. doi: 10.1023/A:1022208302819. - DOI
-
- Clare J, Sreekrishna K, Romanos M. Expression of tetanus toxin fragment C. Methods Mol Biol. 1998;103:193–208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

