Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransport-2 Inhibitors on Blood Pressure in People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 43 Randomized Control Trials With 22 528 Patients
- PMID: 28546454
- PMCID: PMC5669140
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004007
Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransport-2 Inhibitors on Blood Pressure in People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 43 Randomized Control Trials With 22 528 Patients
Abstract
Background: The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a class of oral hypoglycemic agents. We undertake a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies to determine the effect of SGLT2 on blood pressure (BP) among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
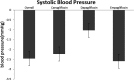
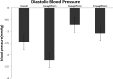
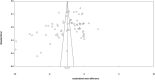
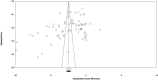
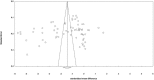
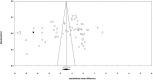
Methods and results: PubMed-Medline, Web of Science, Cochrane Database, and Google Scholar databases were searched to identify trial registries evaluating the impact of SGLT2 on BP. Random-effects models meta-analysis was used for quantitative data synthesis. The meta-analysis indicated a significant reduction in systolic BP following treatment with SGLT2 (weighted mean difference -2.46 mm Hg [95% CI -2.86 to -2.06]). The weighted mean differences for the effect on diastolic BP was -1.46 mm Hg (95% CI -1.82 to -1.09). In these subjects the weighted mean difference effects on serum triglycerides and total cholesterol were -2.08 mg/dL (95% CI -2.51 to -1.64) and 0.77 mg/dL (95% CI 0.33-1.21), respectively. The weighted mean differences for the effect of SGLT2 on body weight was -1.88 kg (95% CI -2.11 to -1.66) across all studies. These findings were robust in sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions: Treatment with SGLT2 glucose cotransporter inhibitors therefore has beneficial off-_target effects on BP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and may also be of value in improving other cardiometabolic parameters including lipid profile and body weight in addition to their expected effects on glycemic control. However, our findings should be interpreted with consideration for the moderate statistical heterogeneity across the included studies.
Keywords: Sodium‐glucose cotransport‐2 inhibitors; blood pressure; diabetes mellitus; meta‐analysis.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 May 18;6(5):e005686. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.005686. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28522675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2016 Oct 27;12:393-405. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S111991. eCollection 2016. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2016. PMID: 27822054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empagliflozin for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Overview of Phase 3 Clinical Trials.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(4):405-423. doi: 10.2174/1573399812666160613113556. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017. PMID: 27296042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Outcomes in Patients Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Feb;10(5):e019463. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019463. Epub 2021 Feb 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33625242 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of canagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, on blood pressure and markers of arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a post hoc analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Feb 27;16(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0511-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28241822 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Changes in Cardiovascular and Renal Biomarkers Associated with SGLT2 Inhibitors Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 25;15(11):2526. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112526. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Haemodynamic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Treatment in Chronic Heart Failure Patients.Card Fail Rev. 2024 Sep 11;10:e09. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2023.25. eCollection 2024. Card Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 39309522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The changes of cardiac energy metabolism with sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor therapy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Dec 6;10:1291450. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1291450. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38124893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors With Fracture Risk in Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Oct 1;4(10):e2130762. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30762. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34705014 Free PMC article.
-
The SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Significantly Improves the Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Function in Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Intern Med. 2018 Aug 1;57(15):2147-2156. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0701-17. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29607968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mazidi M, Heidari‐Bakavoli A, Khayyatzadeh SS, Azarpazhooh MR, Nematy M, Safarian M, Esmaeili H, Parizadeh SM, Ghayour‐Mobarhan M, Kengne AP, Ferns GA. Serum hs‐CRP varies with dietary cholesterol, but not dietary fatty acid intake in individuals free of any history of cardiovascular disease. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016;70:1454–1457. - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Ginsberg HN, Bakris GL, Clark NG, Costa F, Eckel R, Fonseca V, Gerstein HC, Grundy S, Nesto RW. Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in people with diabetes mellitus: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:162–172. - PubMed
-
- Gæde P, Lund‐Andersen H, Parving H‐H, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:580–591. - PubMed
-
- del Cañizo‐Gómez FJ, Moreira‐Andrés MN. Cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: do we follow the guidelines? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;65:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Mazidi M, Karimi E, Rezaie P, Ferns GA. Treatment with GLP1 receptor agonists reduce serum CRP concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;8:77–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

