Oridonin inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis through blocking the Notch signaling
- PMID: 28579904
- PMCID: PMC5447451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2017.04.037
Oridonin inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis through blocking the Notch signaling
Abstract
Background: Oridonin is a diterpenoid isolated from Rabdosia rubescens with potent anticancer activity. The aim of our study is to investigate the role of oridonin to inhibit growth and metastasis of human breast cancer cells.
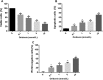
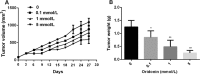
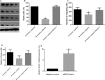
Methods: The effect of oridonin on proliferation was evaluated by MTT assay, cell migration and invasion were evaluated by transwell migration and invasion assays in human breast cancer cells. The inhibitive effect of oridonin in vivo was determined by using xenografted nude mice. In addition, the expression of Notch receptors (Notch 1-4) was detected by western blot.
Results: Oridonin inhibited human breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. In addition, oridonin significantly induced human breast cancer cells apoptosis. Furthermore, the oridonin treatment not only inhibited cancer cell migration and invasion, but more significantly, decreased the expression of Notch 1-4 protein.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the inhibitive effect of oridonin is likely to be driven by the inhibition of Notch signaling pathway and the resulting increased apoptosis.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cell apoptosis; Notch signaling pathway; Oridonin.
Figures
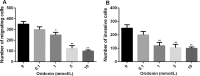
Similar articles
-
Oridonin effectively reverses the drug resistance of cisplatin involving induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of MMP expression in human acute myeloid leukemia cells.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017 Mar;24(3):678-686. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.01.042. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28386196 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic antitumor activity of oridonin and valproic acid on HL-60 leukemia cells.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):5620-5627. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27845. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30320906
-
Oridonin induces apoptosis, inhibits migration and invasion on highly-metastatic human breast cancer cells.Am J Chin Med. 2013;41(1):177-96. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X13500134. Am J Chin Med. 2013. PMID: 23336515
-
Recent advances in oridonin derivatives with anticancer activity.Front Chem. 2023 Feb 9;11:1066280. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1066280. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36846854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oridonin from Rabdosia rubescens: An emerging potential in cancer therapy - A comprehensive review.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Feb 1;12(5):3046-3067. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3986. eCollection 2024 May. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38726411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Products as Anticancer Agents: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2022 Nov 30;27(23):8367. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238367. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo Serum Enabled Production of Ultrafine Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Treatment.Mater Today (Kidlington). 2020 Sep;38:10-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2020.03.005. Epub 2020 May 4. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2020. PMID: 33716549 Free PMC article.
-
Biocompatible Fe-Based Micropore Metal-Organic Frameworks as Sustained-Release Anticancer Drug Carriers.Molecules. 2018 Sep 28;23(10):2490. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102490. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30274195 Free PMC article.
-
Oridonin Dose-Dependently Modulates the Cell Senescence and Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:5023536. doi: 10.1155/2021/5023536. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34795783 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2019 Nov 6;14:48. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0270-9. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31719837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cui Q., Tashiro S., Onodera S., Minami M., Ikejima T. Autophagy preceded apoptosis in oridonin-treated human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007;30:859–864. - PubMed
-
- Feng B., Ashraf M.A., Peng L. Characterization of particle shape, zeta potential, loading efficiency and outdoor stability for chitosan-ricinoleic acid loaded with rotenone. Open Life Sci. 2016;11(1):380–386.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

