Looking to nature for a new concept in antimicrobial treatments: isoflavonoids from Cytisus striatus as antibiotic adjuvants against MRSA
- PMID: 28630440
- PMCID: PMC5476642
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03716-7
Looking to nature for a new concept in antimicrobial treatments: isoflavonoids from Cytisus striatus as antibiotic adjuvants against MRSA
Abstract
The spread of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), has shortened the useful life of anti-staphylococcal drugs enormously. Two approaches can be followed to address this problem: screening various sources for new leads for antibiotics or finding ways to disable the resistance mechanisms to existing antibiotics. Plants are resistant to most microorganisms, but despite extensive efforts to identify metabolites that are responsible for this resistance, no substantial progress has been made. Plants possibly use multiple strategies to deal with microorganisms that evolved over time. For this reason, we searched for plants that could potentiate the effects of known antibiotics. From 29 plant species tested, Cytisus striatus clearly showed such an activity and an NMR-based metabolomics study allowed the identification of compounds from the plant extracts that could act as antibiotic adjuvants. Isoflavonoids were found to potentiate the effect of ciprofloxacin and erythromycin against MRSA strains. For the structure-activity relationship (SAR), 22 isoflavonoids were assessed as antibiotic adjuvants. This study reveals a clear synergy between isoflavonoids and the tested antibiotics, showing their great potential for applications in the clinical therapy of infections with antibiotic-resistant microorganisms such as MRSA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
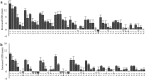
 , 2: additive
, 2: additive  and 3: potentiation effect
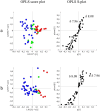
and 3: potentiation effect  ) and 1H-NMR data in the range of the region between δ 6.00 and 8.60 of the different classes of potentiating activity of extracts of C. striatus on ciprofloxacin (a) and erythromycin (b). The sample preparation and extraction conditions were performed as shown in Supplementary Table 2.
) and 1H-NMR data in the range of the region between δ 6.00 and 8.60 of the different classes of potentiating activity of extracts of C. striatus on ciprofloxacin (a) and erythromycin (b). The sample preparation and extraction conditions were performed as shown in Supplementary Table 2.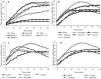
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of baicalein with ciprofloxacin against NorA over-expressed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and inhibition of MRSA pyruvate kinase.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):767-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.06.039. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21782012
-
In Vitro Antistaphylococcal Synergistic Effect of Isoflavone Metabolite Demethyltexasin with Amoxicillin and Oxacillin.Microb Drug Resist. 2018 Jan/Feb;24(1):24-29. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2017.0033. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Microb Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 28570834
-
New erythromycin derivatives enhance β-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015 Apr;60(4):352-8. doi: 10.1111/lam.12378. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25588530
-
Combating against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus - two fatty acids from Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) exhibit synergistic effects with erythromycin.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;67(1):107-16. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12315. Epub 2014 Sep 11. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25212982
-
Marine bacteria: potential sources for compounds to overcome antibiotic resistance.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Jun;97(11):4763-73. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4905-y. Epub 2013 May 3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23640363 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic Potentiation as a Promising Strategy to Combat Macrolide Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;12(12):1715. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12121715. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial activity of resveratrol-derived monomers and dimers against foodborne pathogens.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;9(1):19525. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55975-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31862939 Free PMC article.
-
Plants with Antimicrobial Activity Growing in Italy: A Pathogen-Driven Systematic Review for Green Veterinary Pharmacology Applications.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 8;11(7):919. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070919. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity against Acne-Causing Bacteria and Phytochemical Analysis of Galangal (Alpinia galanga) and Bitter Ginger (Zingiber zerumbet) Extracts.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 10;25(20):10869. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010869. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456652 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic potentiating effect of Bauhinia purpurea L. against multidrug resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 16;15:1385268. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1385268. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38694794 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

