Adiponectin, a Therapeutic _target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction
- PMID: 28635626
- PMCID: PMC5486142
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18061321
Adiponectin, a Therapeutic _target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction
Abstract
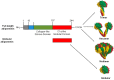
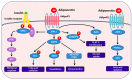
Adiponectin is the most abundant peptide secreted by adipocytes, whose reduction plays a central role in obesity-related diseases, including insulin resistance/type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. In addition to adipocytes, other cell types, such as skeletal and cardiac myocytes and endothelial cells, can also produce this adipocytokine. Adiponectin effects are mediated by adiponectin receptors, which occur as two isoforms (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2). Adiponectin has direct actions in liver, skeletal muscle, and the vasculature.Adiponectin exists in the circulation as varying molecular weight forms, produced by multimerization. Several endoplasmic reticulum ER-associated proteins, including ER oxidoreductase 1-α (Ero1-α), ER resident protein 44 (ERp44), disulfide-bond A oxidoreductase-like protein (DsbA-L), and glucose-regulated protein 94 (GPR94), have recently been found to be involved in the assembly and secretion of higher-order adiponectin complexes. Recent data indicate that the high-molecular weight (HMW) complexes have the predominant action in metabolic tissues. Studies have shown that adiponectin administration in humans and rodents has insulin-sensitizing, anti-atherogenic, and anti-inflammatory effects, and, in certain settings, also decreases body weight. Therefore, adiponectin replacement therapy in humans may suggest potential versatile therapeutic _targets in the treatment of obesity, insulin resistance/type 2 diabetes, and atherosclerosis. The current knowledge on regulation and function of adiponectin in obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease is summarized in this review.
Keywords: adiponectin; endothelial dysfunction; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin--a key adipokine in the metabolic syndrome.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006 May;8(3):264-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2005.00510.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006. PMID: 16634986 Review.
-
[Adiponectin and its role in the pathogenesis of obesity, diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2006 Mar;20(117):355-7. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2006. PMID: 16780274 Review. Polish.
-
Physiological and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Dec;32 Suppl 7:S13-8. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.233. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 19136982 Review.
-
Adiponectin and its potential in the treatment of obesity, diabetes and insulin resistance.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005 Oct;6(10):988-93. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16259219 Review.
-
Adiponectin, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.Biochimie. 2004 Nov;86(11):779-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.09.016. Biochimie. 2004. PMID: 15589686 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of angiogenesis and regenerative lung growth in Lepob/ob mice through adiponectin-VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 16;11:1491971. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1491971. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39479393 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberry (Morus alba L.) ethanol extract attenuates lipid metabolic disturbance and adipokine imbalance in high-fat fed rats.Nutr Res Pract. 2022 Dec;16(6):716-728. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2022.16.6.716. Epub 2022 May 9. Nutr Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36467763 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Roles of Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miRNAs in Obesity-Mediated Insulin Resistance.Adv Nutr. 2021 Mar 31;12(2):566-574. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa105. Adv Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32879940 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties of Fermented Plant Foods.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 30;13(5):1516. doi: 10.3390/nu13051516. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33946303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for the Neuronal Expression and Secretion of Adiponectin.Cells. 2022 Sep 1;11(17):2725. doi: 10.3390/cells11172725. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078135 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

