Local lung hypoxia determines epithelial fate decisions during alveolar regeneration
- PMID: 28737769
- PMCID: PMC5600325
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3580
Local lung hypoxia determines epithelial fate decisions during alveolar regeneration
Abstract
After influenza infection, lineage-negative epithelial progenitors (LNEPs) exhibit a binary response to reconstitute epithelial barriers: activating a Notch-dependent ΔNp63/cytokeratin 5 (Krt5) remodelling program or differentiating into alveolar type II cells (AEC2s). Here we show that local lung hypoxia, through hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF1α), drives Notch signalling and Krt5pos basal-like cell expansion. Single-cell transcriptional profiling of human AEC2s from fibrotic lungs revealed a hypoxic subpopulation with activated Notch, suppressed surfactant protein C (SPC), and transdifferentiation toward a Krt5pos basal-like state. Activated murine Krt5pos LNEPs and diseased human AEC2s upregulate strikingly similar core pathways underlying migration and squamous metaplasia. While robust, HIF1α-driven metaplasia is ultimately inferior to AEC2 reconstitution in restoring normal lung function. HIF1α deletion or enhanced Wnt/β-catenin activity in Sox2pos LNEPs blocks Notch and Krt5 activation, instead promoting rapid AEC2 differentiation and migration and improving the quality of alveolar repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
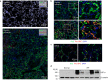
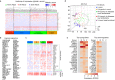
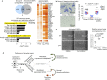
Comment in
-
Lung Alveolar Repair: Not All Cells Are Equal.Trends Mol Med. 2017 Oct;23(10):871-873. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28870601
Similar articles
-
Lineage-negative progenitors mobilize to regenerate lung epithelium after major injury.Nature. 2015 Jan 29;517(7536):621-5. doi: 10.1038/nature14112. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25533958 Free PMC article.
-
p63(+)Krt5(+) distal airway stem cells are essential for lung regeneration.Nature. 2015 Jan 29;517(7536):616-20. doi: 10.1038/nature13903. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25383540 Free PMC article.
-
Rare SOX2+ Airway Progenitor Cells Generate KRT5+ Cells that Repopulate Damaged Alveolar Parenchyma following Influenza Virus Infection.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Nov 8;7(5):817-825. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27773701 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulation in the adaptive process to hypoxia in lung epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Mar;296(3):L267-74. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90528.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19118091 Review.
-
Lung cancer stem cells: progress and prospects.Cancer Lett. 2013 Sep 10;338(1):89-93. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.08.014. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 22906416 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Basal-Like Cell-Conditioned Medium Exerts Anti-Fibrotic Effects In Vitro and In Vivo.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 8;10:844119. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.844119. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35350187 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary endogenous progenitor stem cell subpopulation: Physiology, pathogenesis, and progress.J Intensive Med. 2022 Oct 22;3(1):38-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2022.08.005. eCollection 2023 Jan 31. J Intensive Med. 2022. PMID: 36789358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of Airway Epithelial Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Cells. 2022 Mar 19;11(6):1050. doi: 10.3390/cells11061050. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence of alveolar epithelial progenitor cells: a critical driver of lung fibrosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):C483-C495. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00239.2023. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37458437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alveolar epithelial regeneration in the aging lung.J Clin Invest. 2023 Oct 16;133(20):e170504. doi: 10.1172/JCI170504. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37843280 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA193455/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL117600/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084376/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007185/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL131817/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL051856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL111054/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128484/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008339/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL131817/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

