Expert Coaching in Weight Loss: Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 29535082
- PMCID: PMC5871741
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.9738
Expert Coaching in Weight Loss: Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
Background: Providing coaches as part of a weight management program is a common practice to increase participant engagement and weight loss success. Understanding coach and participant interactions and how these interactions impact weight loss success needs to be further explored for coaching best practices.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to analyze the coach and participant interaction in a 6-month weight loss intervention administered by Retrofit, a personalized weight management and Web-based disease prevention solution. The study specifically examined the association between different methods of coach-participant interaction and weight loss and tried to understand the level of coaching impact on weight loss outcome.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using 1432 participants enrolled from 2011 to 2016 in the Retrofit weight loss program. Participants were males and females aged 18 years or older with a baseline body mass index of ≥25 kg/m², who also provided at least one weight measurement beyond baseline. First, a detailed analysis of different coach-participant interaction was performed using both intent-to-treat and completer populations. Next, a multiple regression analysis was performed using all measures associated with coach-participant interactions involving expert coaching sessions, live weekly expert-led Web-based classes, and electronic messaging and feedback. Finally, 3 significant predictors (P<.001) were analyzed in depth to reveal the impact on weight loss outcome.
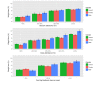
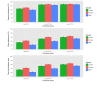
Results: Participants in the Retrofit weight loss program lost a mean 5.14% (SE 0.14) of their baseline weight, with 44% (SE 0.01) of participants losing at least 5% of their baseline weight. Multiple regression model (R2=.158, P<.001) identified the following top 3 measures as significant predictors of weight loss at 6 months: expert coaching session attendance (P<.001), live weekly Web-based class attendance (P<.001), and food log feedback days per week (P<.001). Attending 80% of expert coaching sessions, attending 60% of live weekly Web-based classes, and receiving a minimum of 1 food log feedback day per week were associated with clinically significant weight loss.
Conclusions: Participant's one-on-one expert coaching session attendance, live weekly expert-led interactive Web-based class attendance, and the number of food log feedback days per week from expert coach were significant predictors of weight loss in a 6-month intervention.
Keywords: body mass index; coaching; feedback; obesity; overweight; weight loss; weight reduction program.
©Stefanie Lynn Painter, Rezwan Ahmed, Robert F Kushner, James O Hill, Richard Lindquist, Scott Brunning, Amy Margulies. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 13.03.2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: SP, RA, SB, and AM are employees of Retrofit, Inc, with equity in the company. JH, RK, and RL are active members of the Retrofit, Inc Advisory Board, with equity in the company.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personalized Web-Based Weight Loss Behavior Change Program With and Without Dietitian Online Coaching for Adults With Overweight and Obesity: Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Nov 5;22(11):e17494. doi: 10.2196/17494. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33151151 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
What Matters in Weight Loss? An In-Depth Analysis of Self-Monitoring.J Med Internet Res. 2017 May 12;19(5):e160. doi: 10.2196/jmir.7457. J Med Internet Res. 2017. PMID: 28500022 Free PMC article.
-
Retrofit Weight-Loss Outcomes at 6, 12, and 24 Months and Characteristics of 12-Month High Performers: A Retrospective Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2016 Aug 22;4(3):e101. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.5873. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2016. PMID: 27549134 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: An Updated Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. PMID: 30354042 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Football Fans in Training (FFIT): a randomised controlled trial of a gender-sensitised weight loss and healthy living programme for men – end of study report.Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Jan. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Jan. PMID: 25654156 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
A Mobile-Based Nutrition Tracker App Enhanced Dietitian-Guided 2:1:1 Diet-Induced Weight Loss: An 8-Week Retrospective Cohort Study in Taiwan.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 19;16(14):2331. doi: 10.3390/nu16142331. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064777 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions of employees with a low and medium level of education towards workplace health promotion programmes: a mixed-methods study.BMC Public Health. 2022 Aug 25;22(1):1617. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13976-2. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36008851 Free PMC article.
-
The Assessment of a Personalized Nutrition Tool (eNutri) in Germany: Pilot Study on Usability Metrics and Users' Experiences.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Aug 4;6(8):e34497. doi: 10.2196/34497. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35925664 Free PMC article.
-
From Young to Older, the 4 Phases Method Is Efficient in Promoting Quick Weight, BMI, and Waist Circumference Reductions.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 27;10(8):1398. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10081398. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893221 Free PMC article.
-
Pragmatic Evaluation of a Health System-Based Employee Weight Management Program.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 31;18(11):5901. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115901. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34072841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/ 6wjWaAWcr
-
- Waters H, DeVol R. Milken Institute. Weighing Down America: The Health and Economic Impact of Obesity http://www.milkeninstitute.org/publications/view/833 6vfARXaLA.
-
- National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2016 https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/hus/index.htm 6vdJUOX2i.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical