Co-delivery of Aurora-A inhibitor XY-4 and Bcl-xl siRNA enhances antitumor efficacy for melanoma therapy
- PMID: 29563798
- PMCID: PMC5849942
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S147759
Co-delivery of Aurora-A inhibitor XY-4 and Bcl-xl siRNA enhances antitumor efficacy for melanoma therapy
Abstract
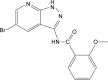
Background: The newly synthesized Aurora-A kinase inhibitor XY-4 is a potential anti-cancer agent, but its hydrophobicity and limited efficiency restrict further application. Nanotechnology based combined therapy provides an optimized strategy for solving these issues.
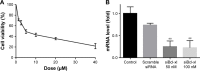
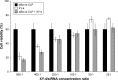
Methods: In this study, the newly synthesized Aurora-A kinase inhibitor XY-4 and Bcl-xl _targeted siRNA were co-delivered by cationic liposomes, creating an injectable co-delivery formulation. The anti-cancer ability and mechanisms of XY-4/Bcl-xl siRNA co-loaded cationic liposomes were studied both in vitro and in vivo.
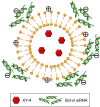
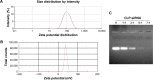
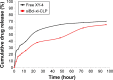
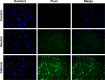
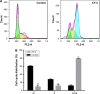
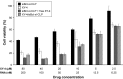
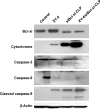
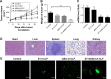
Results: The prepared liposomes had a mean particle size of 91.3±4.5 nm with a zeta potential of 38.5±0.5 mV and were monodispersed (Polydispersity index =0.183) in water solution, with high drug loading capacity and stability. Intriguingly, the positive charges of co-delivery liposomes not only facilitated gene delivery, but also obviously enhanced drug uptake. The XY-4/Bcl-xl siRNA co-loaded cationic liposomes demonstrated enhanced anti-cancer effects on B16 melanoma cells in vitro by activation mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Moreover, intratumoral injection of this co-delivery formulation efficiently inhibited the growth of a B16 melanoma xenograft model in vivo.
Conclusion: By co-delivering Aurora-A kinase inhibitor XY-4 and Bcl-xl _targeting siRNA in a nanoformulation, our study supplied a potential combination strategy for melanoma therapy.
Keywords: Aurora-A kinase inhibitor; RNA interference; apoptosis; co-delivery; liposome; melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Gray-Schopfer V, Wellbrock C, Marais R. Melanoma biology and new _targeted therapy. Nature. 2007;445(7130):851–857. - PubMed
-
- Lapenna S, Giordano A. Cell cycle kinases as therapeutic _targets for cancer. Nature Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(7):547–566. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

