Reduced White Matter Integrity With Cognitive Impairments in End Stage Renal Disease
- PMID: 29725309
- PMCID: PMC5917068
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00143
Reduced White Matter Integrity With Cognitive Impairments in End Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
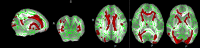
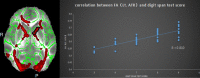
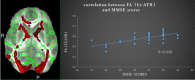
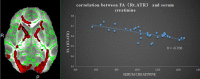
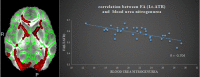
Background: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is a serious public health problem, which can often lead to multiorgan dysfunction, such as cerebrovascular disease and cognitive damage. It is essential to understand cognitive impairment in patients with ESRD to develop better ESRD treatment and prevent further cognitive impairment. Cognitive impairment is believed to be related to structural abnormalities in the brain. Purpose: To investigate white matter microstructural abnormalities in patients with ESRD using TBSS analysis of DTI and to explore the possible mechanisms underlying the impaired cognitive function. Materials and Methods: A TBSS analysis of DTI data was to investigate the microstructural changes in their WM over the whole brain. We chose the white matter tracts or regions with significantly reduced FA as the regions of interest (ROIs), Pearson's correlations were performed between clinical indicators (Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), digit span task scores, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen and hemodialysis duration) and the mean FA value of the ROIs in the ESRD patients. Results: Lower FA and higher MD, AD and RD values were observed in widespread and symmetrical WM in ESRD patients than healthy controls (HCs), Pearson correlation analysis revealed a significantly positive correlation between the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores and FA values in the right corona radiata and left anterior thalamic radiation (ATR) and demonstrated a significantly negative correlation between FA values and the serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen in the ATR (P < 0.01) in addition, digit span task scores positively correlate with the FA value in the left anterior rather than in the corona radiata. No cluster survived when we adopted the False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction to multiple comparisons. Conclusion: Our study indicate widespread impairment of the white matter in ESRD patients. Damage to the thalamic radiation and corona radiata may affect cognitive function in ESRD patients, the reduced integrity of ATR may tend to affect the working memory while the damage to the corona radiata may involve the executive function impaired in ESRD patients. The accumulation of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen may contribute to the WM impairment.
Keywords: blood urea nitrogen; cognitive function; end-stage renal disease; serum creatinine; tract-based spatial statistics; white matter.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Segmental Abnormalities of White Matter Microstructure in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: An Automated Fiber Quantification Tractography Study.Front Neurosci. 2021 Dec 6;15:765677. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.765677. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34938154 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced White Matter Integrity in Patients With End-Stage and Non-end-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease: A Tract-Based Spatial Statistics Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Dec 10;15:774236. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.774236. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955791 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced white matter integrity and cognitive deficits in maintenance hemodialysis ESRD patients: a diffusion-tensor study.Eur Radiol. 2015 Mar;25(3):661-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3466-5. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Eur Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25326436
-
Diffuse interstitial brain edema in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: a tract-based spatial statistics study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2014 Dec;93(28):e313. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000313. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014. PMID: 25526483 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral white matter injury in haemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional tract-based spatial statistics and fixel-based analysis.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Sep 16;17(10):sfae286. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae286. eCollection 2024 Oct. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39398351 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk factors for neurocognitive impairment and the relation with structural brain abnormality in children and young adults with severe chronic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 Jun;38(6):1957-1969. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05781-1. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36322259 Free PMC article.
-
Segmental Abnormalities of White Matter Microstructure in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: An Automated Fiber Quantification Tractography Study.Front Neurosci. 2021 Dec 6;15:765677. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.765677. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34938154 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced White Matter Integrity in Patients With End-Stage and Non-end-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease: A Tract-Based Spatial Statistics Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Dec 10;15:774236. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.774236. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955791 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the dialysis on the white matter tracts in patients with end-stage renal disease using differential tractography study.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 16;13(1):20064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47533-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37973892 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal white matter along fibers by automated fiber quantification in patients undergoing hemodialysis.Neurol Sci. 2023 Dec;44(12):4499-4509. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06912-8. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37393206
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

