Shining a light on cell signaling in leukemia through proteomics: relevance for the clinic
- PMID: 29898608
- PMCID: PMC6444923
- DOI: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1487781
Shining a light on cell signaling in leukemia through proteomics: relevance for the clinic
Abstract
Although cure rates for acute leukemia have steadily improved over the past decades, leukemia remains a deadly disease. Enhanced risk stratification and new therapies are needed to improve outcome. Extensive genetic analyses have identified many mutations that contribute to the development of leukemia. However, most mutations occur infrequently and most gene alterations have been difficult to _target. Most patients have more than one driver mutation in combination with secondary mutations, that result in a leukemic transformation via the alteration of proteins. The proteomics of acute leukemia could more directly identify proteins to facilitate risk stratification, predict chemoresistance and aid selection of therapy. Areas covered: This review discusses aberrantly expressed proteins identified by mass spectrometry and reverse phase protein arrays and their relationship to survival. In addition, we will discuss proteins in the context of functionally related protein groups. Expert commentary: Proteomics is a powerful tool to analyze protein abundance and functional alterations simultaneously for large numbers of patients. In the forthcoming years, validation of tools to quickly assess protein levels to enable routine rapid profiling of proteins with differential abundance and functional activation may be used as adjuncts to aid in therapy selection and to provide additional prognostic insights.
Keywords: Leukemia; Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA); biomarkers (or) biomarker discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

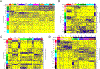
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of reverse phase protein array (RPPA)-based pathway-activation profiling in 84 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines as platform for cancer proteomics and biomarker discovery.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1844(5):950-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.11.017. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24361481
-
Reverse phase protein arrays in acute leukemia: investigative and methodological challenges.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Dec;18(12):1087-1097. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.2020655. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34965151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
_targeted therapy in acute myeloid leukemia: current status and new insights from a proteomic perspective.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2020 Jan;17(1):1-10. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2020.1717951. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31945303 Review.
-
Using reverse-phase protein arrays as pharmacodynamic assays for functional proteomics, biomarker discovery, and drug development in cancer.Semin Oncol. 2016 Aug;43(4):476-83. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Semin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27663479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathway profiling using reverse-phase protein array and its clinical applications.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017 Jul;14(7):607-615. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1344101. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28621158 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum proteomics screening intercellular adhesion molecule-2 improves intermediate-risk stratification in acute myeloid leukemia.Ther Adv Hematol. 2022 Oct 28;13:20406207221132346. doi: 10.1177/20406207221132346. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Hematol. 2022. PMID: 36324489 Free PMC article.
-
Application of High Throughput Technologies in the Development of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Therapy: Challenges and Progress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 5;23(5):2863. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052863. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35270002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics technologies for cancer liquid biopsies.Mol Cancer. 2022 Feb 15;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01526-8. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35168611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ward E, DeSantis C, Robbins A, Kohler B, Jemal A. Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 64(2), 83–103 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Lwenberg B, Ossenkoppele GJ, van Putten W et al. High-dose daunorubicin in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med 361(13), 1235–48 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
